Renovation and Extension Building Costs for Homeowners
Homeowners often embark on renovation and extension projects to transform their living spaces, increase property value, and meet changing needs.

1: Types of Renovations and Extensions
Before delving into costs, homeowners should identify the type of renovation or extension they plan to undertake. Common projects include: Steph Fanizza, Architectural Design & Team Manager
Tell us about your plan and we'll send you a free quote! It takes less than 60 seconds!
1.1. Interior Renovation:
– This involves updating or remodeling existing rooms, such as kitchens, bathrooms, or living areas. Costs vary depending on the scope of work, including new fixtures, finishes, and structural changes.
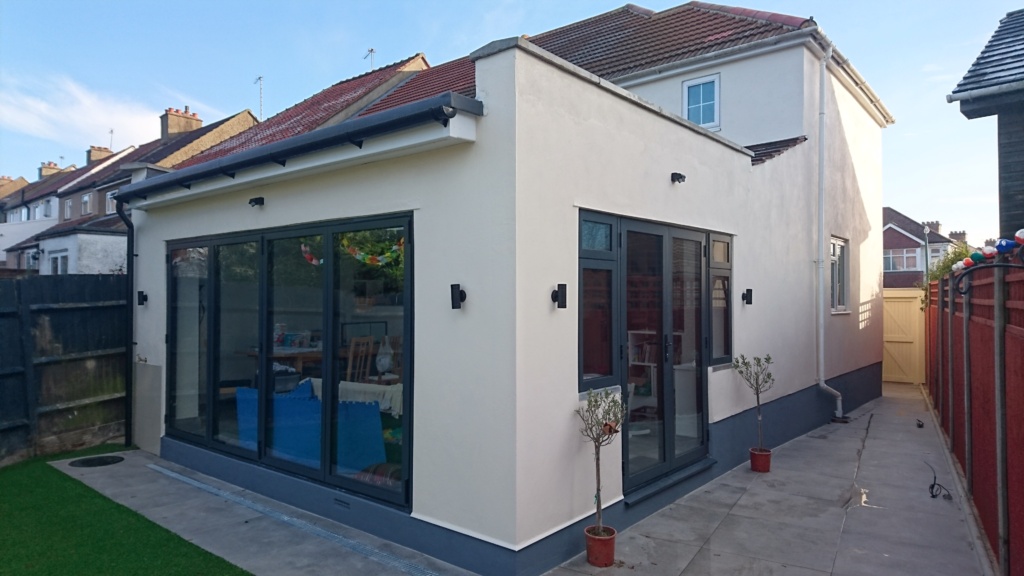
1.2. Single-Storey Extension:
– Extending the ground floor can create additional living space. Costs depend on factors like size, materials, and complexity.
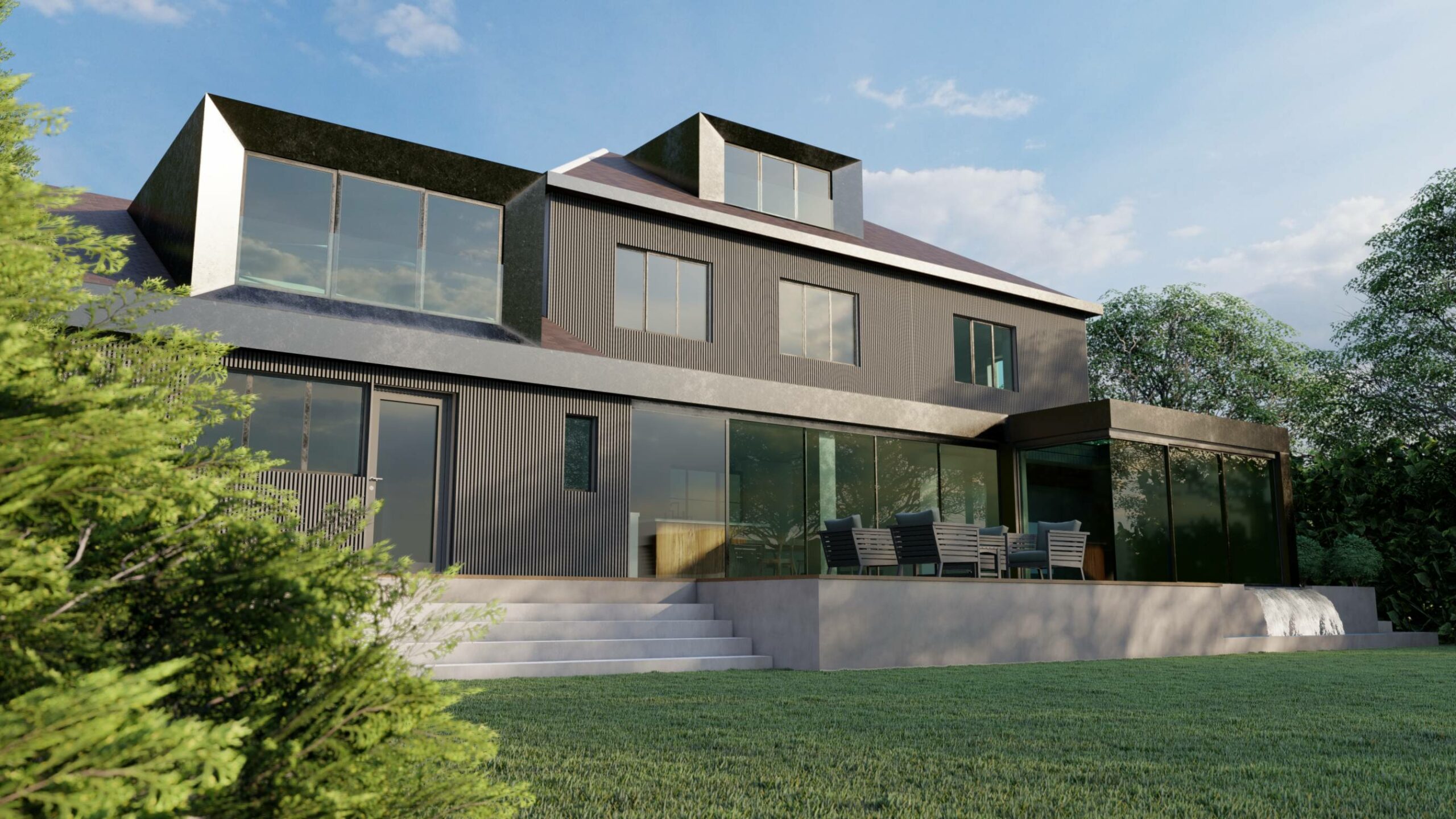
1.3. Two-Storey Extension:
– Extending both the ground and first floors offers even more space but tends to be pricier due to structural considerations.
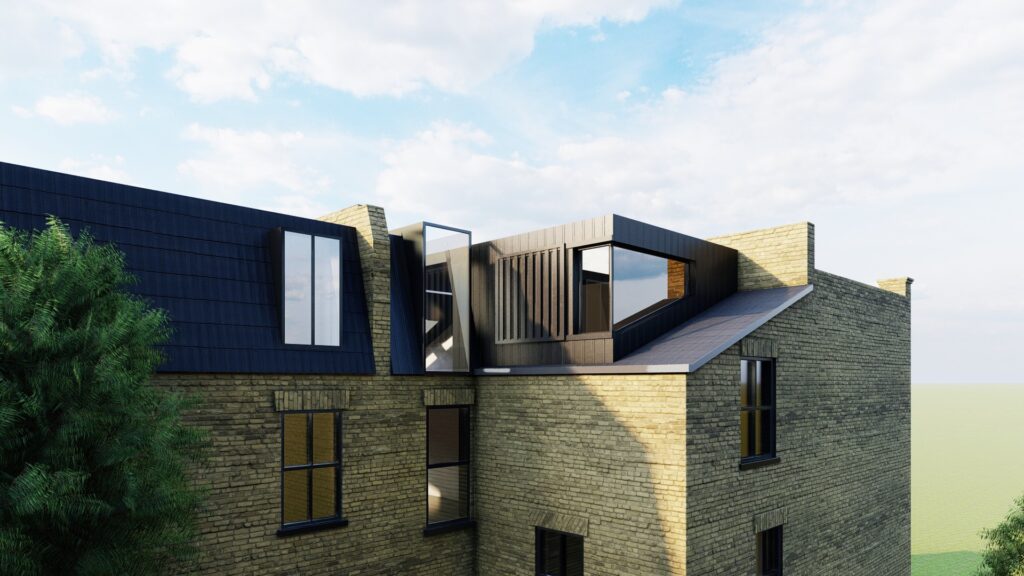
1.4. Loft Conversion:
– Converting an attic into a functional living area is a cost-effective way to add space. Costs depend on the type of conversion and required structural modifications.
1.5. Basement Conversion:
– Turning a basement or cellar into a living space may involve extensive work like waterproofing and insulation, impacting costs.
2: Factors Influencing Costs
2.1. Size and Complexity:
– Larger renovations/extensions and complex designs naturally incur higher costs. This includes factors like the number of rooms, structural changes, and unique features.
2.2. Location:
– Local building regulations, labor costs, and material prices vary by location, impacting project costs.
2.3. Materials:
– The choice of materials, from basic to high-end, significantly influences costs. Durable and energy-efficient materials may have higher upfront costs but provide long-term savings.
2.4. Labor:
– Labor costs are a substantial part of any project budget. Skilled tradespeople and contractors may charge more, but their expertise ensures quality work.
2.5. Permits and Approvals:
– Obtaining necessary permits and approvals adds to the project’s expenses. Budget for application fees, inspections, and potential delays.
3: Estimating Costs
3.1. Budget Allocation:
– Set a realistic budget by considering your financial capacity, expected return on investment, and the scope of the project.
3.2. Professional Consultation:
– Consult architects, builders, or contractors for accurate cost estimates tailored to your project’s specifics.
3.3. Contingency:
– Include a contingency fund (typically 10-20% of the total budget) to cover unforeseen expenses or changes during the project.
4: Financing Options
4.1. Savings:
– Using personal savings is a straightforward way to finance your project. Ensure you have enough set aside to cover costs.
4.2. Home Equity Loans or Lines of Credit:
– Borrowing against your home’s equity can provide substantial funds for renovations or extensions.
4.3. Construction Loans:
– Short-term construction loans offer financing during the project’s duration, with repayment typically after completion.
4.4. Refinancing:
– Refinancing your mortgage can provide funds for renovations by rolling the costs into a new mortgage.
Conclusion
Renovation and extension projects can breathe new life into your home, but they require careful consideration of costs. By understanding the factors that influence expenses, establishing a realistic budget, and exploring financing options, homeowners can successfully navigate their projects while achieving their desired results. Working closely with professionals and being prepared for unexpected costs will help ensure a smooth and satisfying renovation or extension experience.