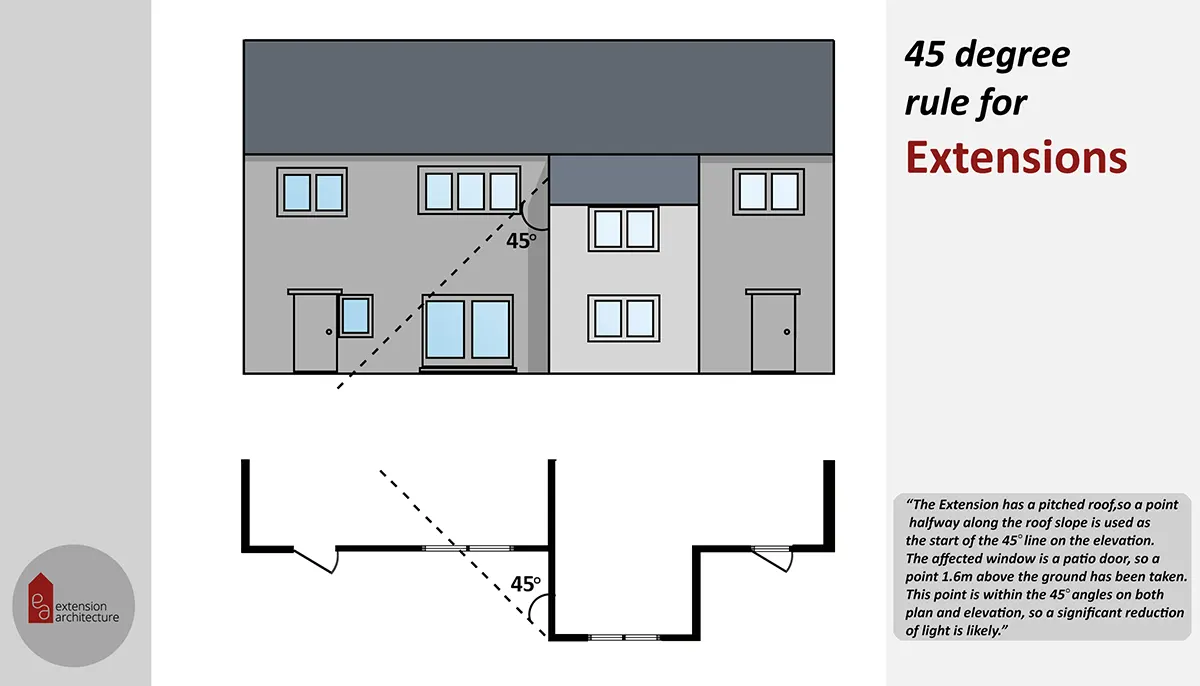
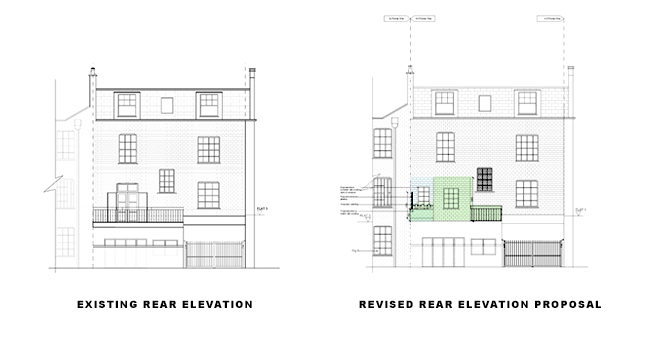
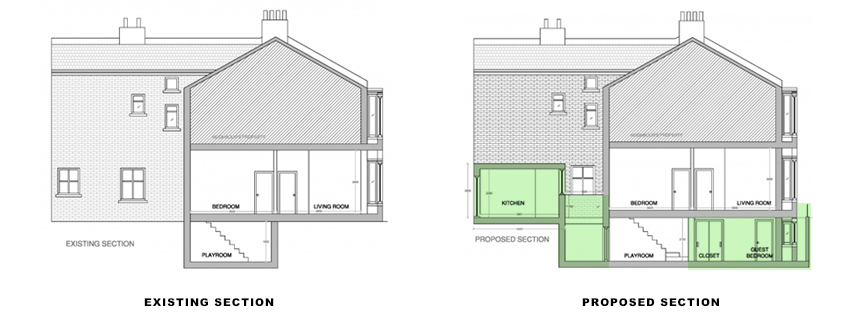
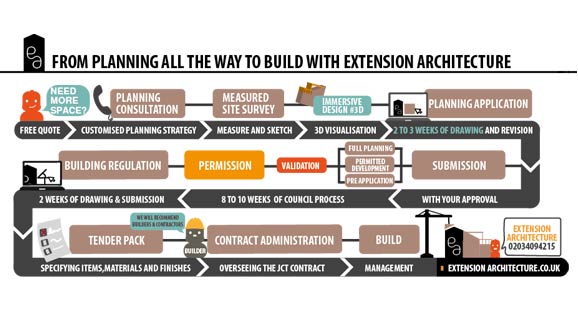
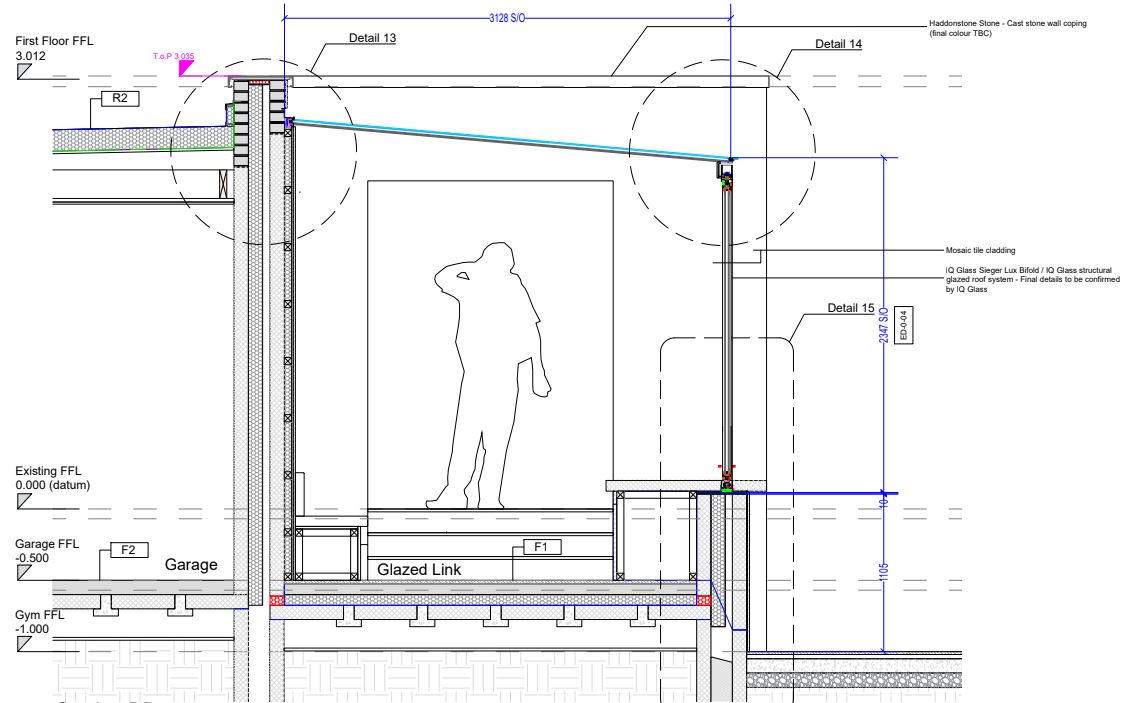
2025 Creative Budget Friendly Small Garden Inspiration Ideas
If you are one among those who find joy in pampering the lush greenery in your backyard, then you constitute the majority of the UK population. Yes, close to 88% of the UK population have a garden in their home. Close to half of the UK adult population have said that they like spending time in their garden if they are not involved in household chores or professional jobs.
For some gardening activities offer a sense of relaxation, satisfaction, and peace of mind. For some, it is an opportunity to convert it into a functional space where they can cultivate for their daily necessity. Depending on the size of your garden, you may choose how you want your garden to be and what you would want to foster in it.
With living spaces becoming premium in most residences across the UK, people who are passionate about gardening activities are making wonders with their small garden spaces. However, designing a small garden is not that easy. There are challenges when you want to do more in a small space without a cluttered feel.
Not everyone may have the space for a large garden. For example, gardens in London are quite small compared to other parts of the UK. Smaller gardens still are spacious enough to grow your daily needs. From vegetable shrubs to enchanting flowers, and decorative to simplistic, get inspired by these diy small garden ideas on a budget and create your own green oasis where you live.
1. Go Vertical
The common challenge with small gardens is the compactness in width. But does that mean we cannot think the other way around? Vertical gardening!
All you need to do is to create a backframe for climbers. Honeysuckle and Clematis are native British climbers and the latter especially fruitions the flowers into varied colours and shapes. The wisteria and climbing rose when grouped offer a strikingly beautiful sight. The Ivy, when planted in groups, can make your garden a bird nester.
Apart from climbers you can also hang pots or baskets to a wall vertically or you can create concrete hollow blocks on the wall with space to grow tiny shrubs and plants. Grab some binding wires (iron or steel), screws, a wooden board, plastic pots, some cement and water.
2. Bush Vegetables
One of the most productive diy small garden ideas on a budget. Planting bush vegetables can be the perfect choice for small and compact gardens as they are grown at lower levels and require less space. A golden opportunity to make your garden your daily vegetable market. Beans, Beetroot, Salad leaves, Chili Peppers, Courgettes, Horseradish, Saltbush Mulberry, Chives, all can be easily grown in a small garden space.
3. Use Containers on Ground
Small garden ideas can come in any form. Try filling those plastic containers with plants and space them around the patio. Let it be a mixture of leafy shrubs and flowers. Let the containers too vary in height to offer the feel of a real garden.
4. Create Small Partitions
A small garden space doesn’t mean you have to rush more plants in it to make it look full and blossoming. Most of them err when they try to fill every inch of their small garden space in an effort to make big with little. This will limit space for patios or pathways and ultimately results in poor maintenance.
On the contrary, create small partitions as confined spaces to grow shrubs, a space for grass turf and another space to rejuvenate and relax with colourful furniture. Create a patio or a pathway to access all of these. It will not only make your small garden look neat, but surprisingly it will also look spacious without you knowing.
5. Seat and Store in One Place
Save more space in your small garden. Let your seating also hold your gardening equipment beneath. Place it in a space such that you gain maximum view of the garden when you feel like unwinding. Make sure the seating space is also at an arm’s distance to a tap to connect the hose pipe.
6. Near a Window
Yes, have you thought of it yet? Though it is wall mounted, the gardening boxes can be placed below your room or kitchen window whichever connects to your garden. It makes for easier access and hence maintenance. Such placements are ideal for low-growing edibles such as salad leaves and berries or mint leaves and basil leaves as climbers.
7. Pergolas
Pergolas are always charming regardless of the garden size. If you have the space decorate the pergola with climbing flowers. A pergola adds space to your garden and connects the indoors of the house to the outdoors. If you can add a roof like covering on top of it, you can even create space below for leisure as well as add space to grow climbing fruits like berries on top.
8. Ornament your Garden
Let your garden be a fulfilling one. Make way for those chirping birds and insects to find a habitat inside your garden. Bird feeders are readily available structures and attract birds of all kinds. Imagine your garden filled with those chirping sounds and happy movements of those colourful birds.
You can also add a small pond like feature inside your garden space. The movement of water makes a soothing sound and adds a calming presence to your garden. In addition, you can also grow water plants inside the pond which will make it a functional feature too.
9. One Dramatic Feature
Let there be one feature that creates that gives way for theatricality inside your garden. It can be anything elemental or symbolic of an ideology or an idea you most believe in. This will make you feel intensely connected to the space.
Conclusion:
Making the most of your small garden space is more about the thought than about the expense. Garden spaces need not be lavishly spent upon. All they require is a great conception and perception. Positioning, selection of artificial elements, choice of shrubs and flowers, they all create an impact. Not matter if it takes days or weeks to finalise on a plan but do it constructively and thoughtfully, your smallest garden can become a big part of your house for your relaxation and peace; a haven away from urban chaos.
At Extension Architecture, we have many more diy small garden ideas on a budget that may excite you. If you are planning to build a garden and have space or are looking for space, call us for a consultation. We may just be able to help you find that secret spot for your greatest rejuvenation. Contact us to know more!