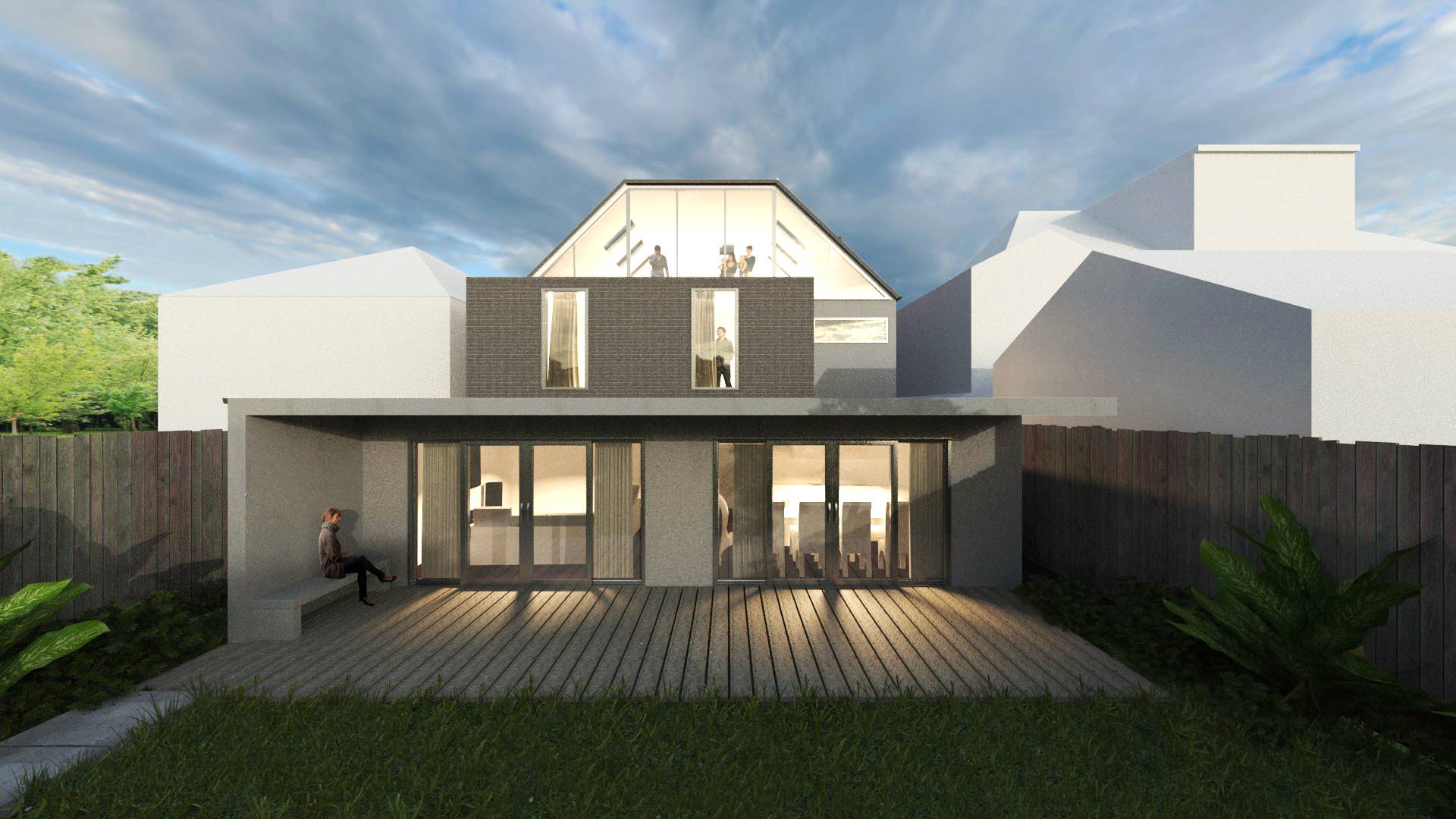
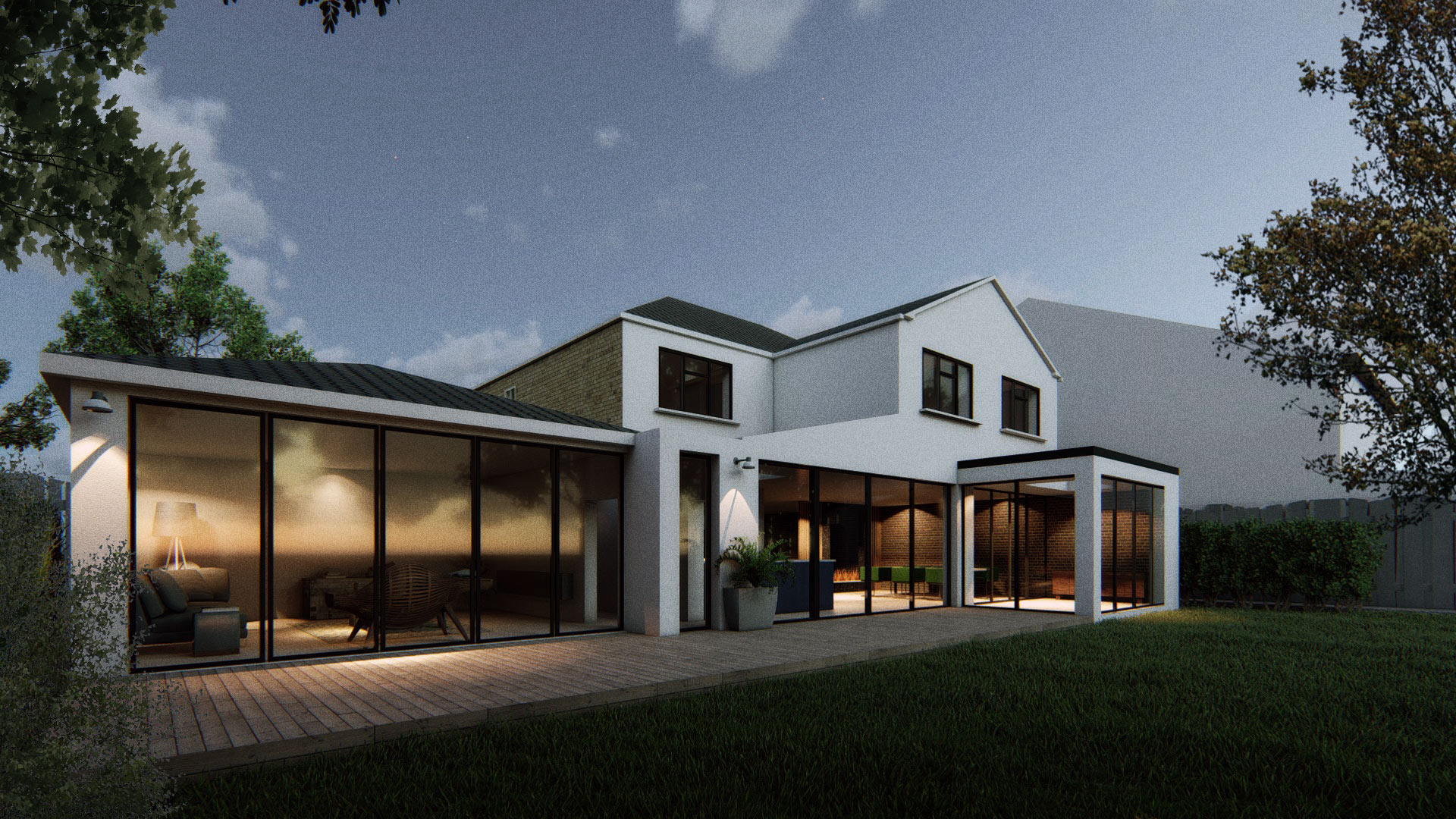
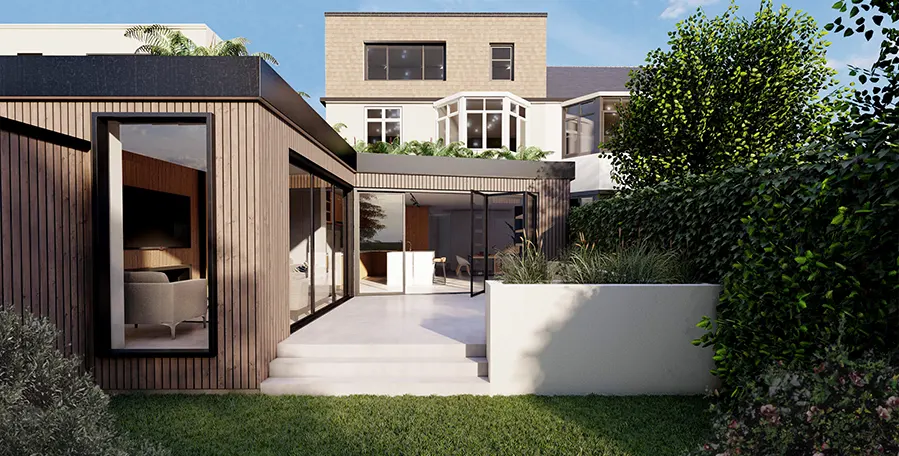
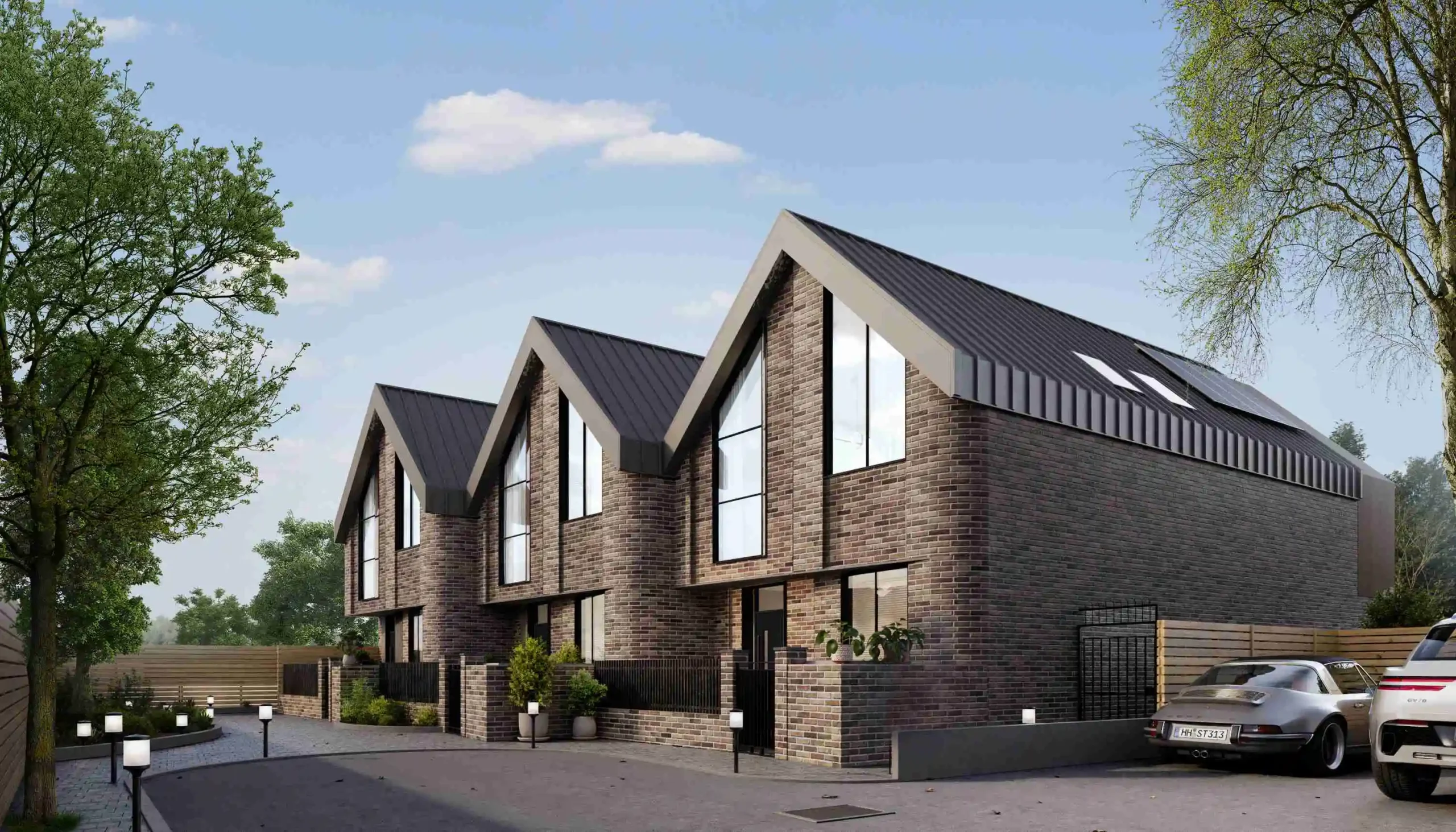
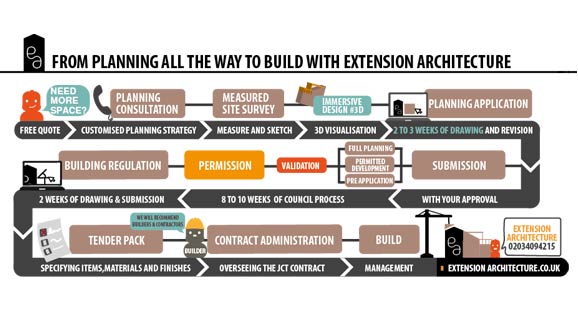
A Comprehensive Guide to Timber Frame Constructions

The UK government has targeted to increase the production of homegrown timber to reach its commitment of delivering 1.5 million homes. The aim is to not just deliver to solve the housing crisis, but to do it with sustainable and efficient methods.
According to the NHBC data, the UK timber frame construction market is expected to reach a market share of 27% by this year. Interestingly, the UK government too is speeding up initiatives to achieve its target of building 1.5 million homes, and a big part of this initiative is to increase timber production.
It’s all looking like a great story coming together for a sustainable & hopeful future. With a lot going on, including ongoing research on new methods of construction, diversification of usage, and types of applications, one can safely say that in the present day, timber frame constructions have spiced up the building & construction sector like no other.
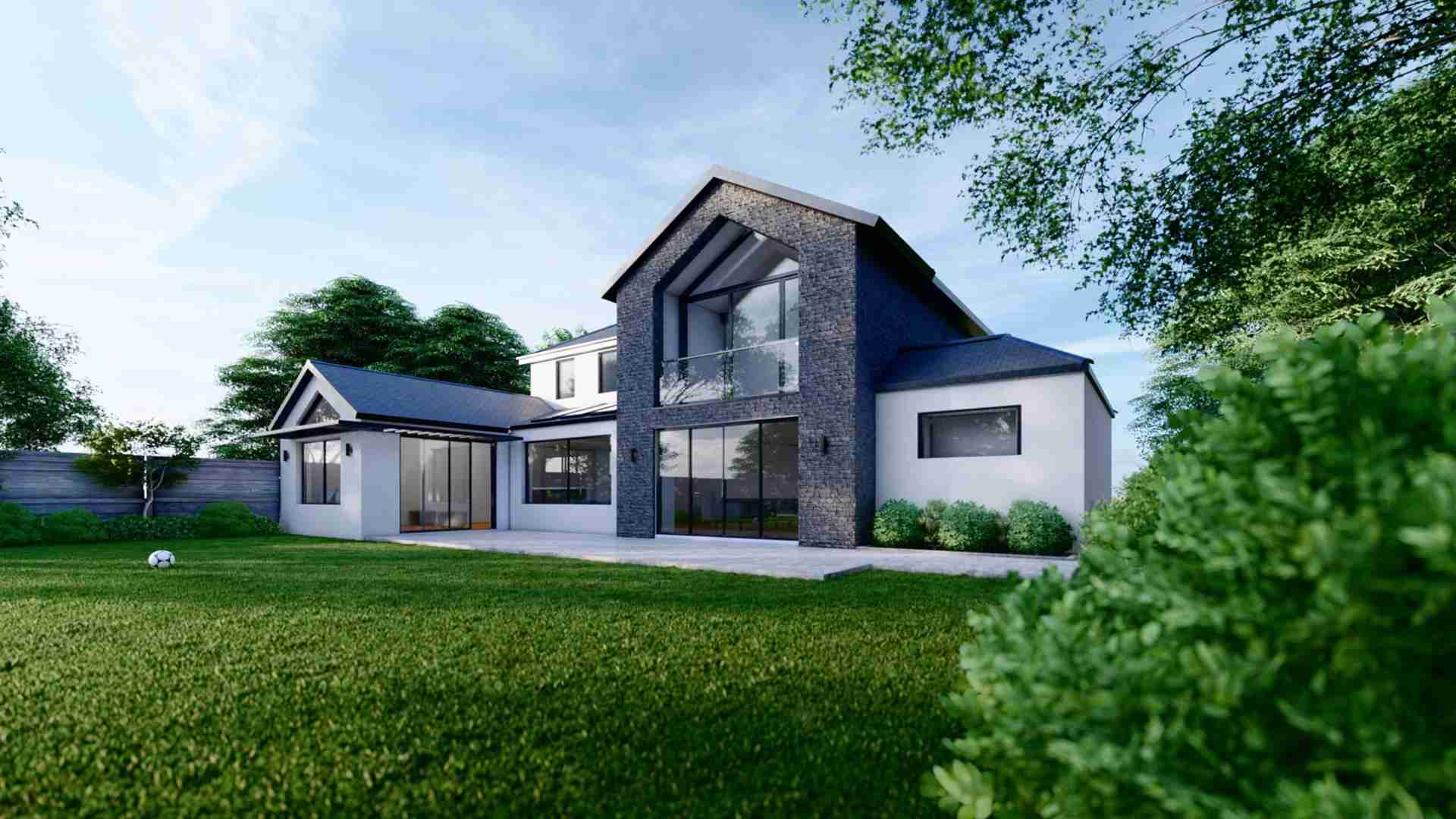
What is a Timber Frame Construction?
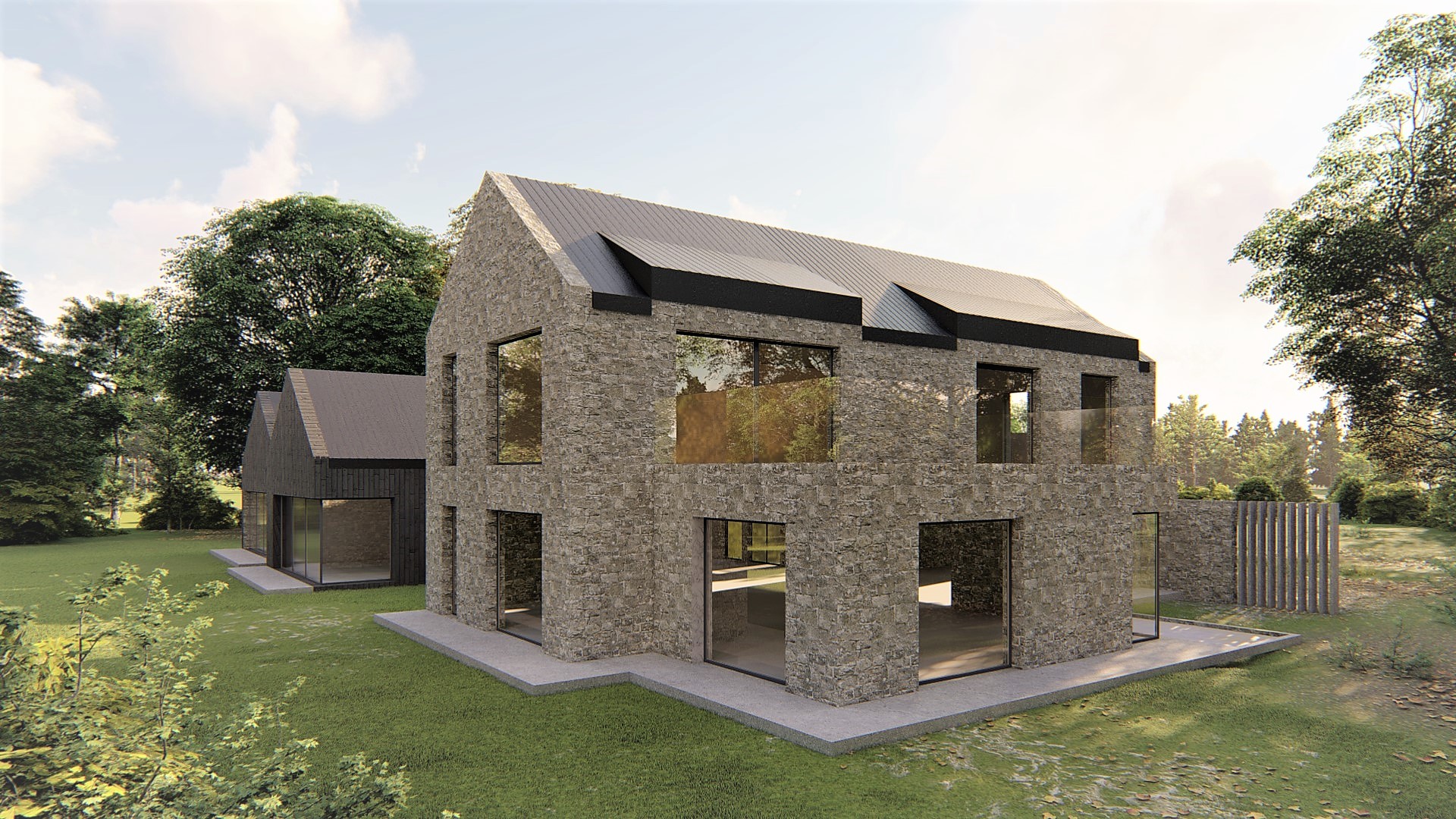
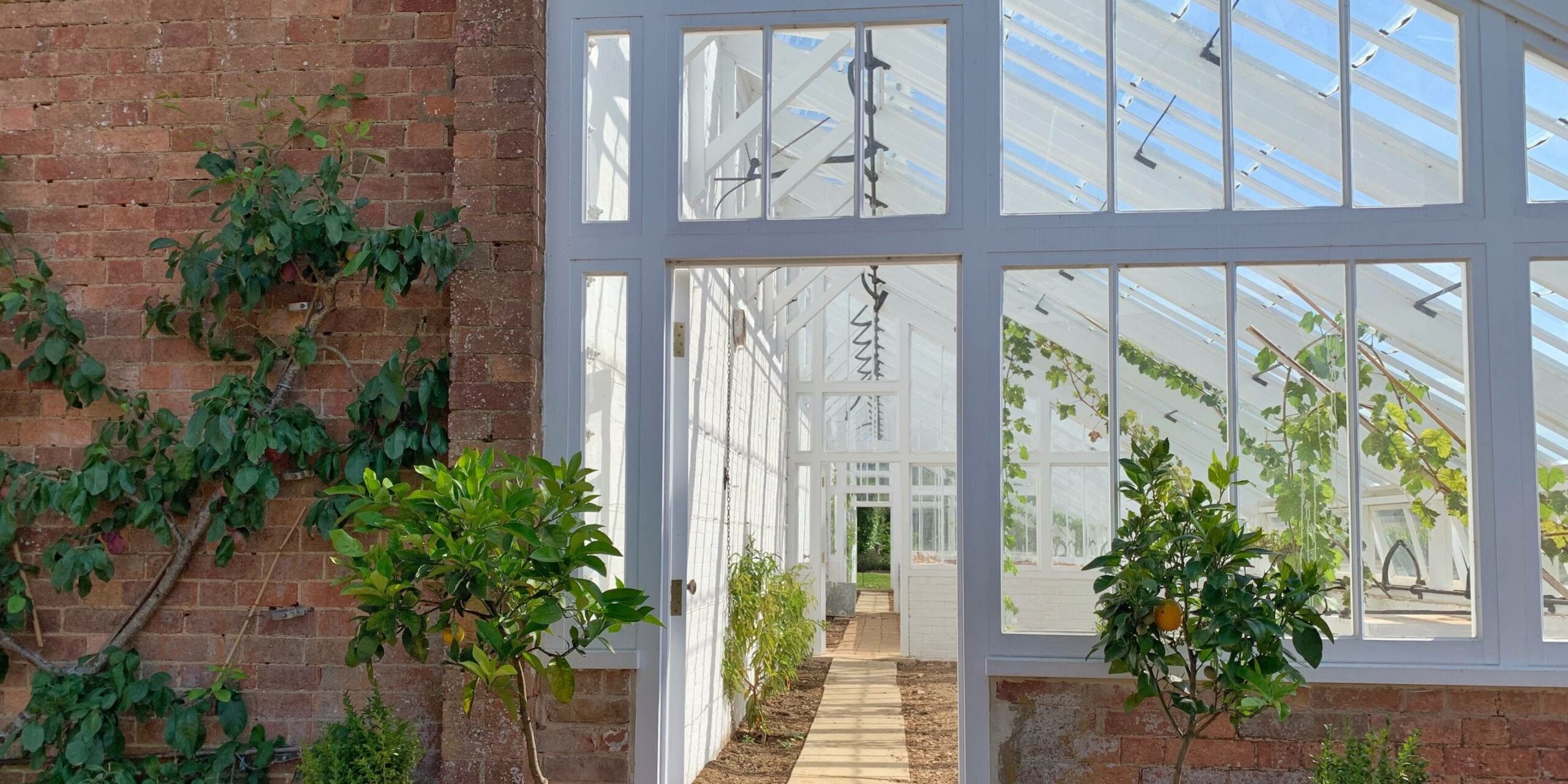
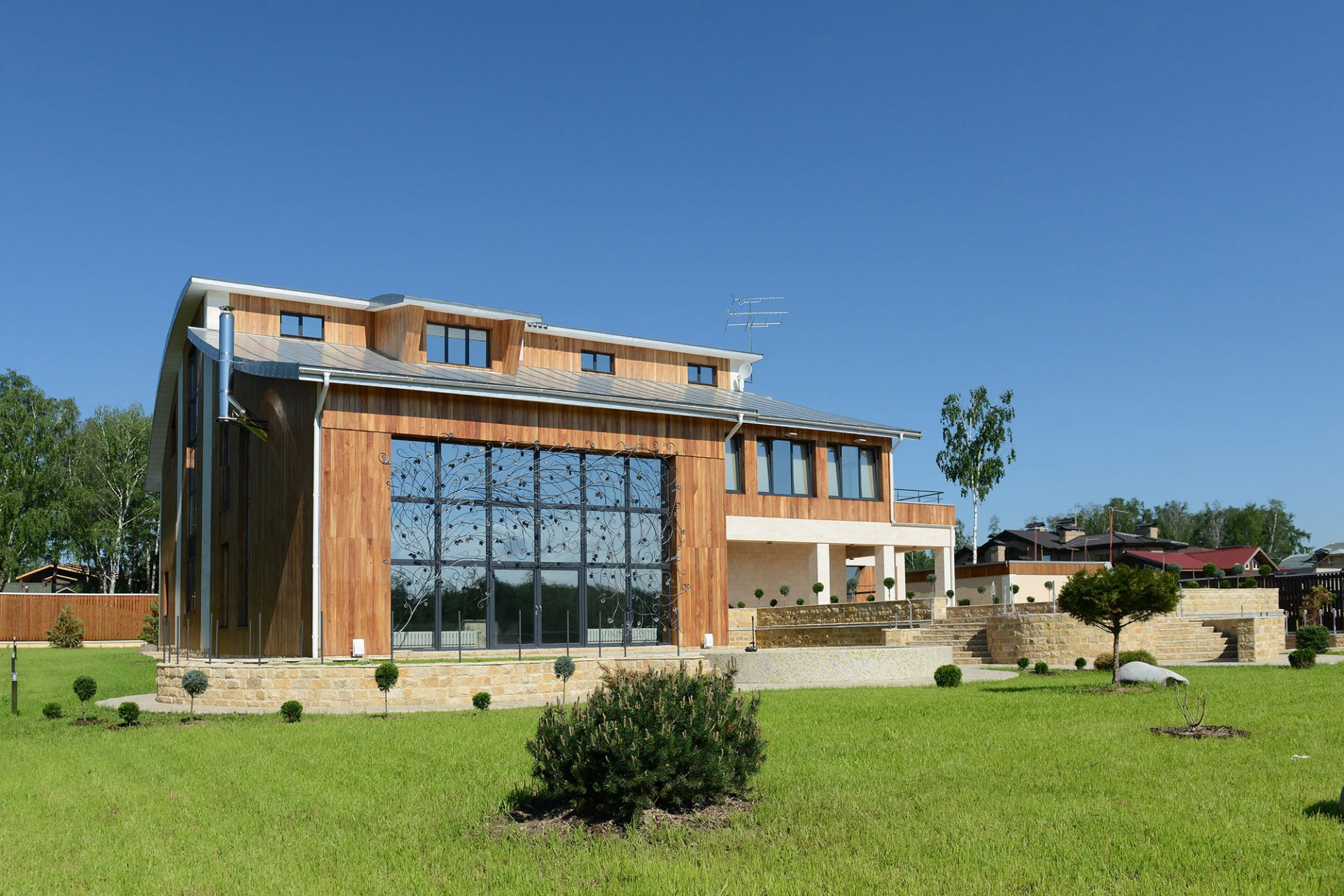
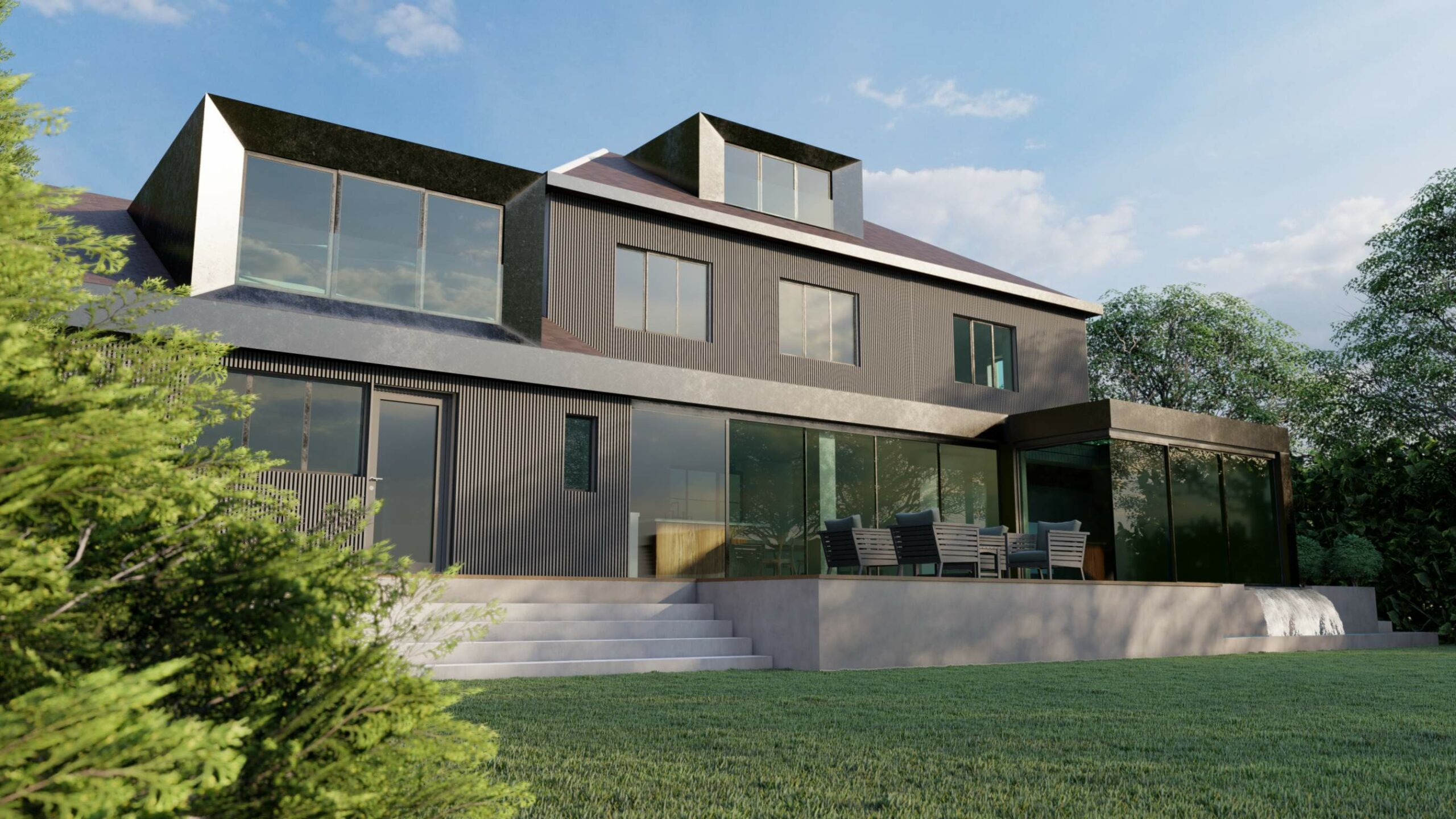
In the present day, timber frame constructions are becoming popular for their energy efficiency, speed of construction, and lower labour costs. Their popularity is much owed to their nature of being extremely eco-friendly as they are great at absorbing carbon properties and are hence considered as one of the most efficient & sustainable choices when it comes to building & construction.
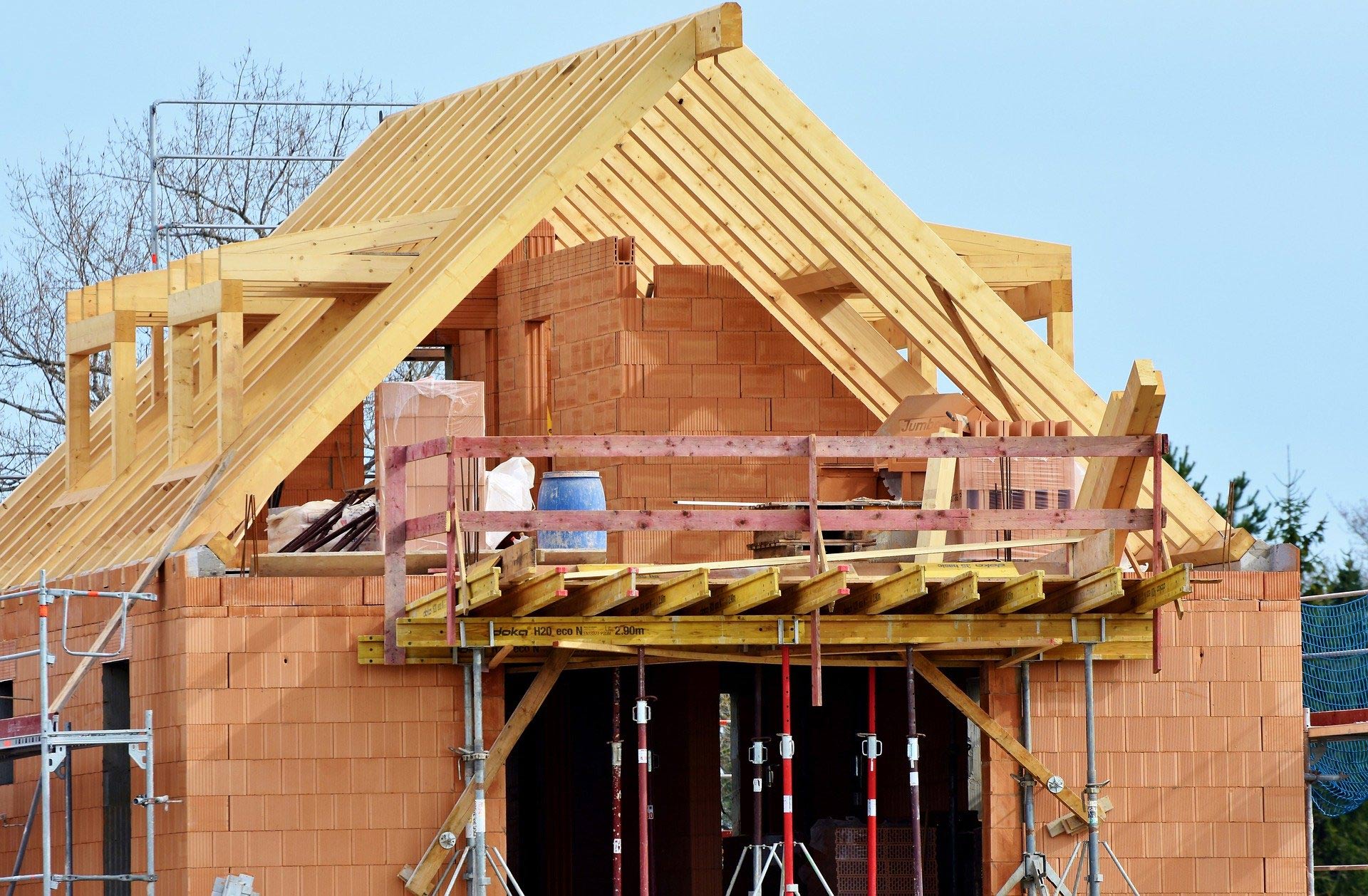
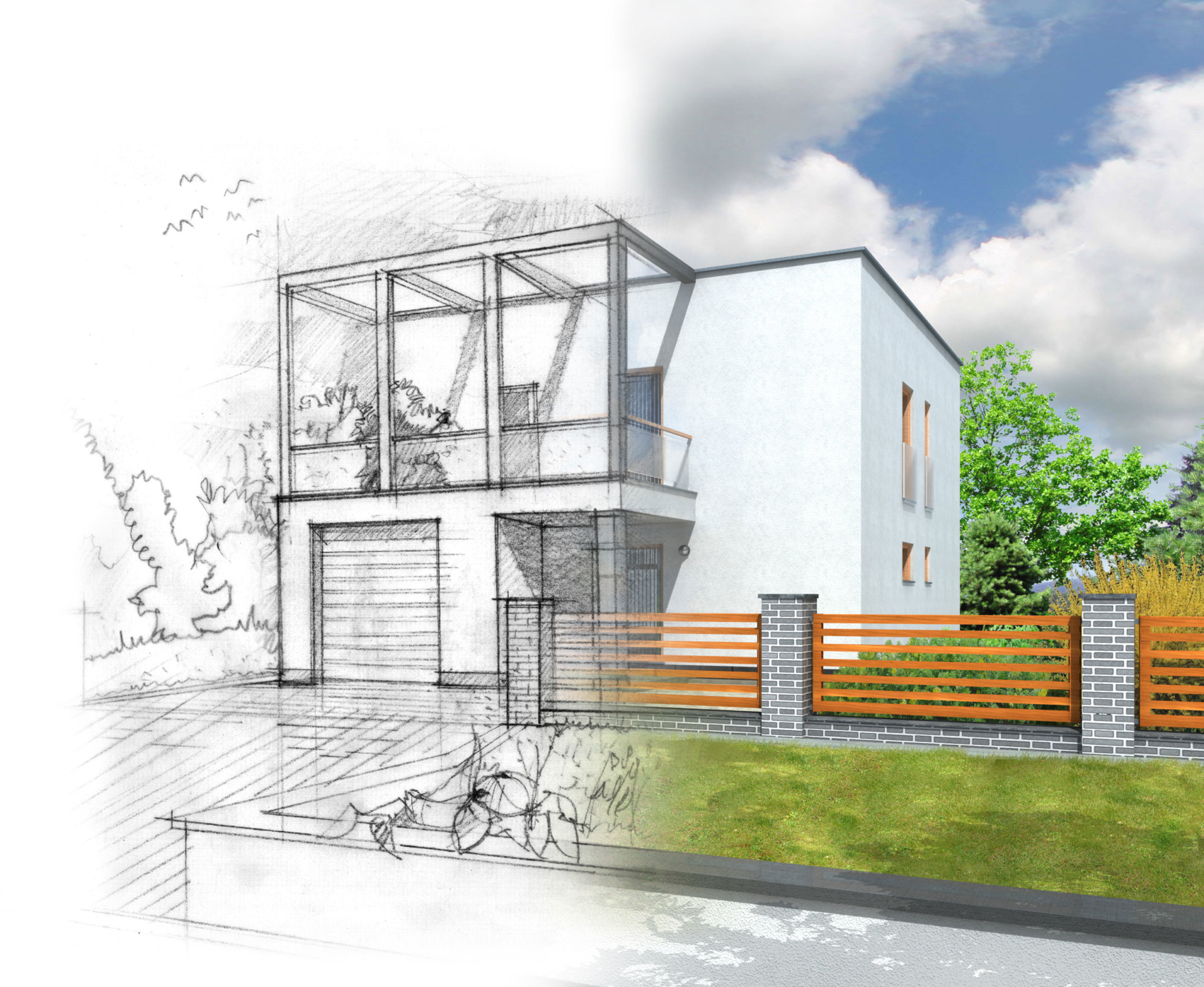
How are Timber Frame Houses Constructed?
Below is a detailed breakdown of how they are built –
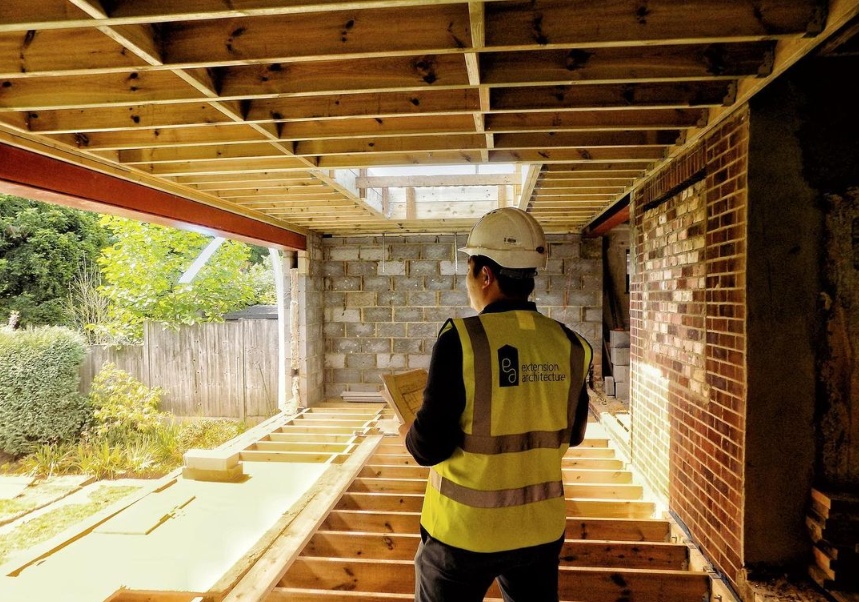
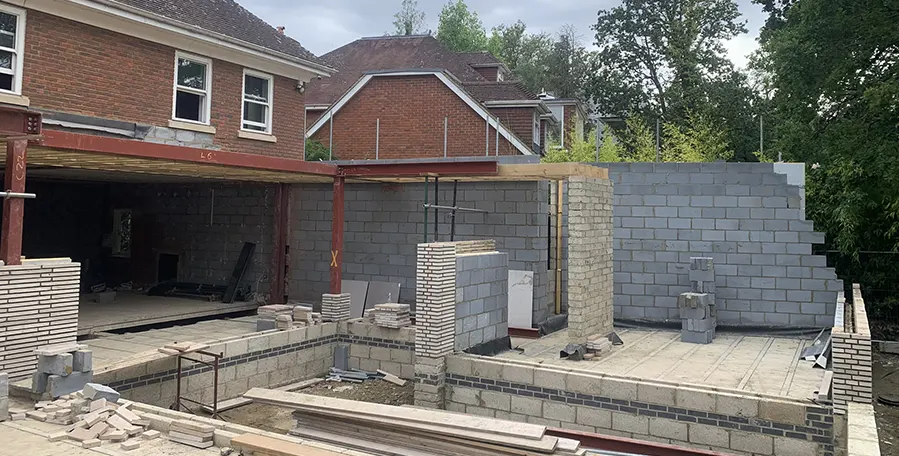
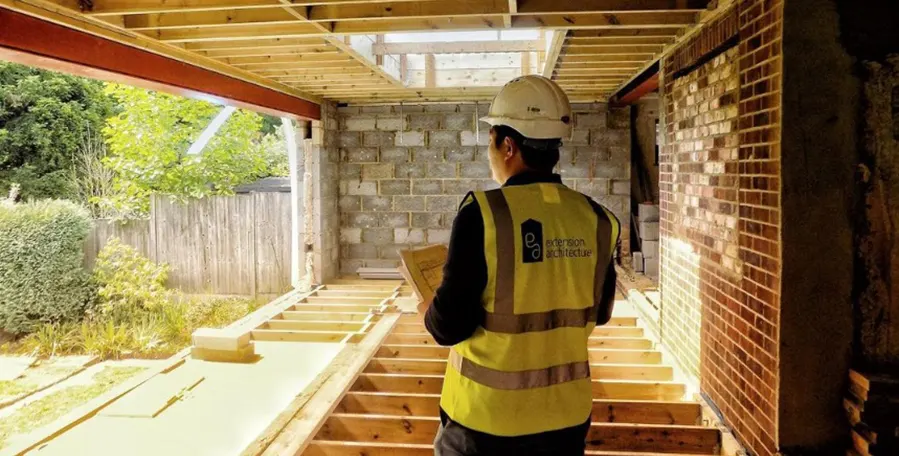
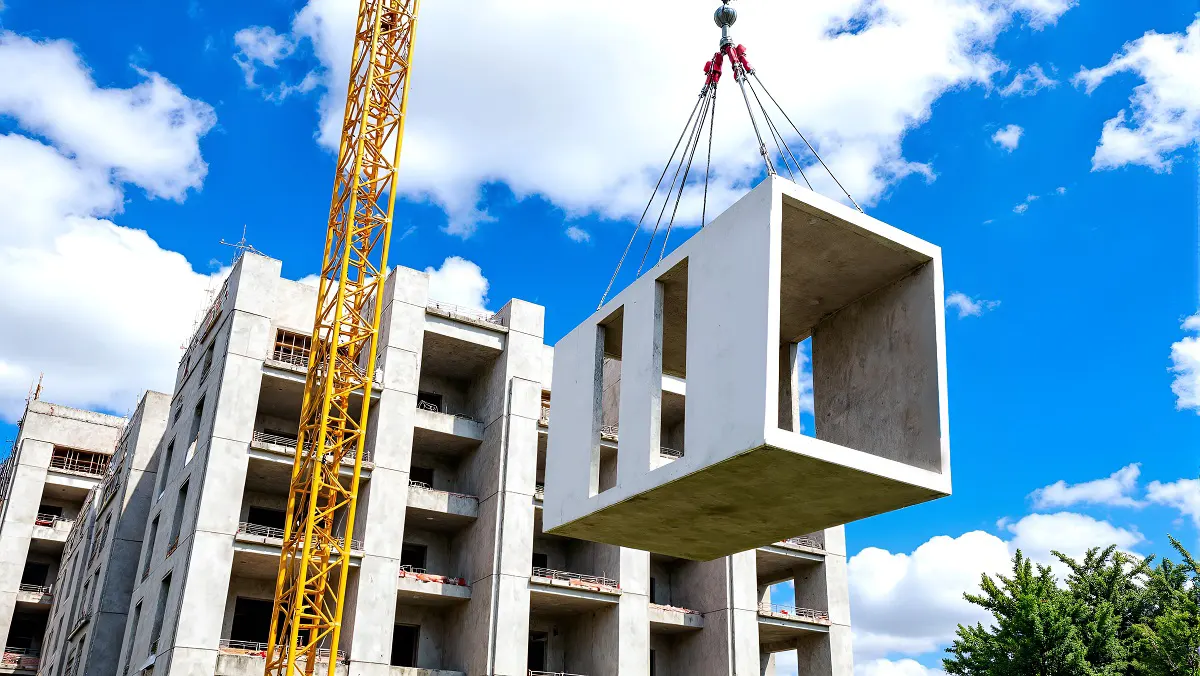
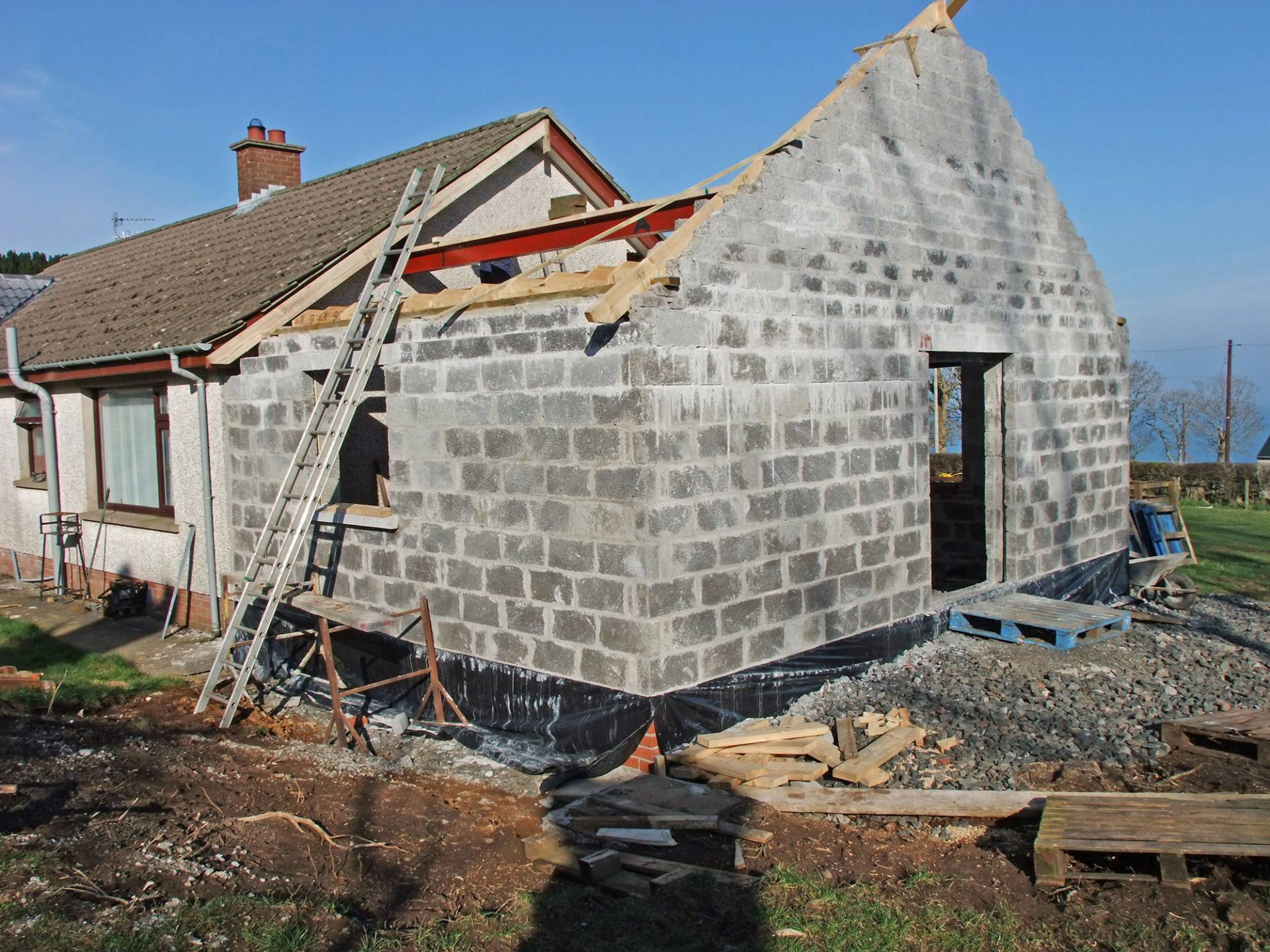
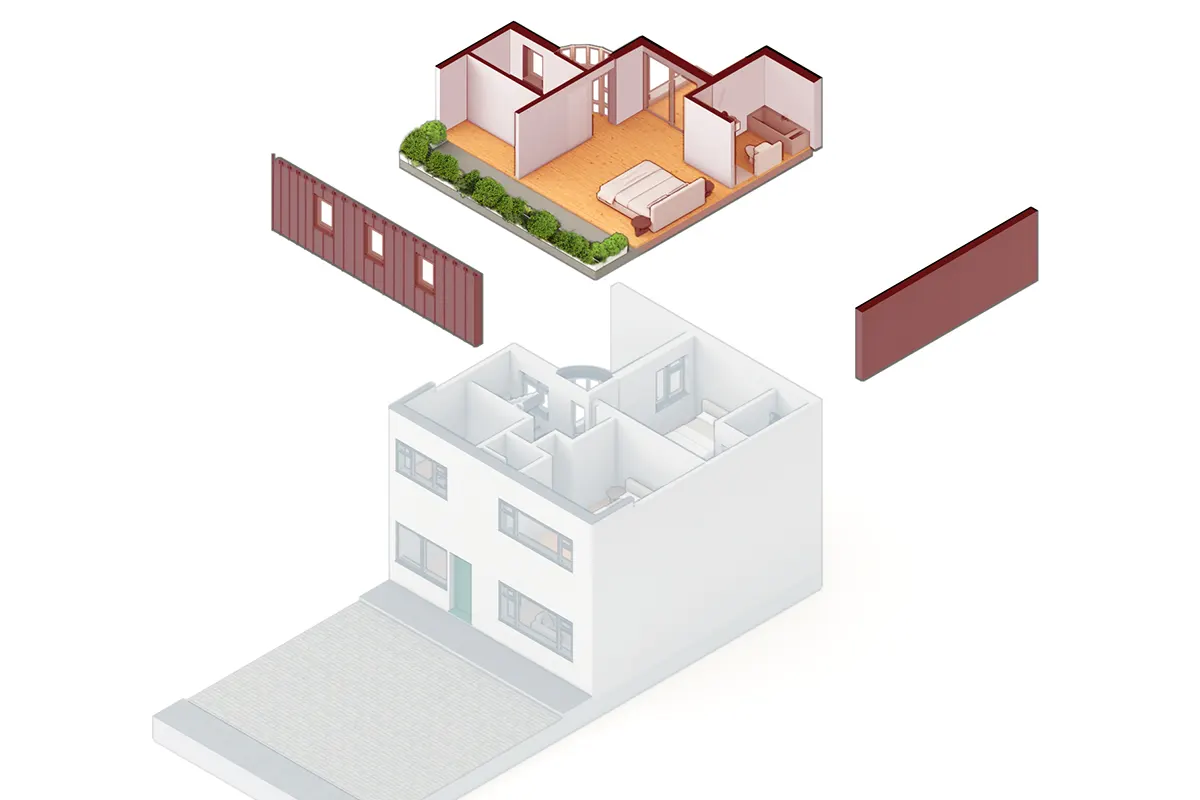
1. Prefabrication
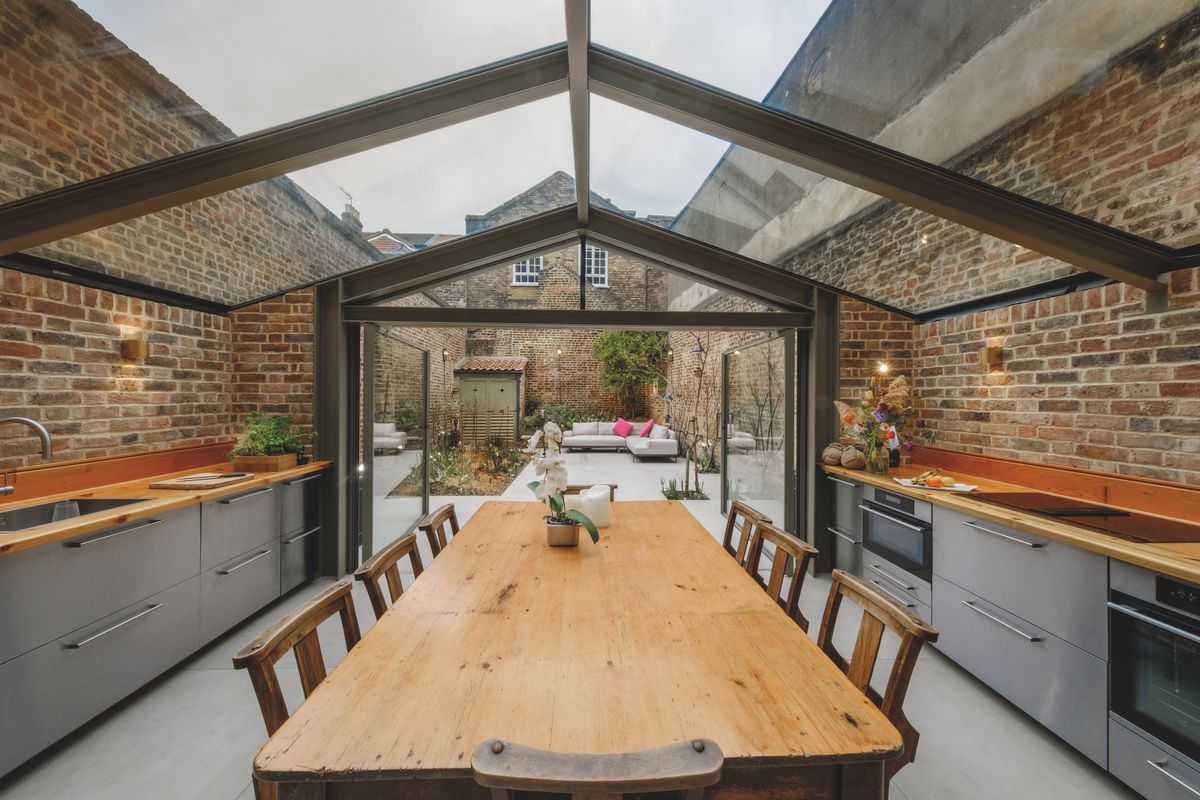
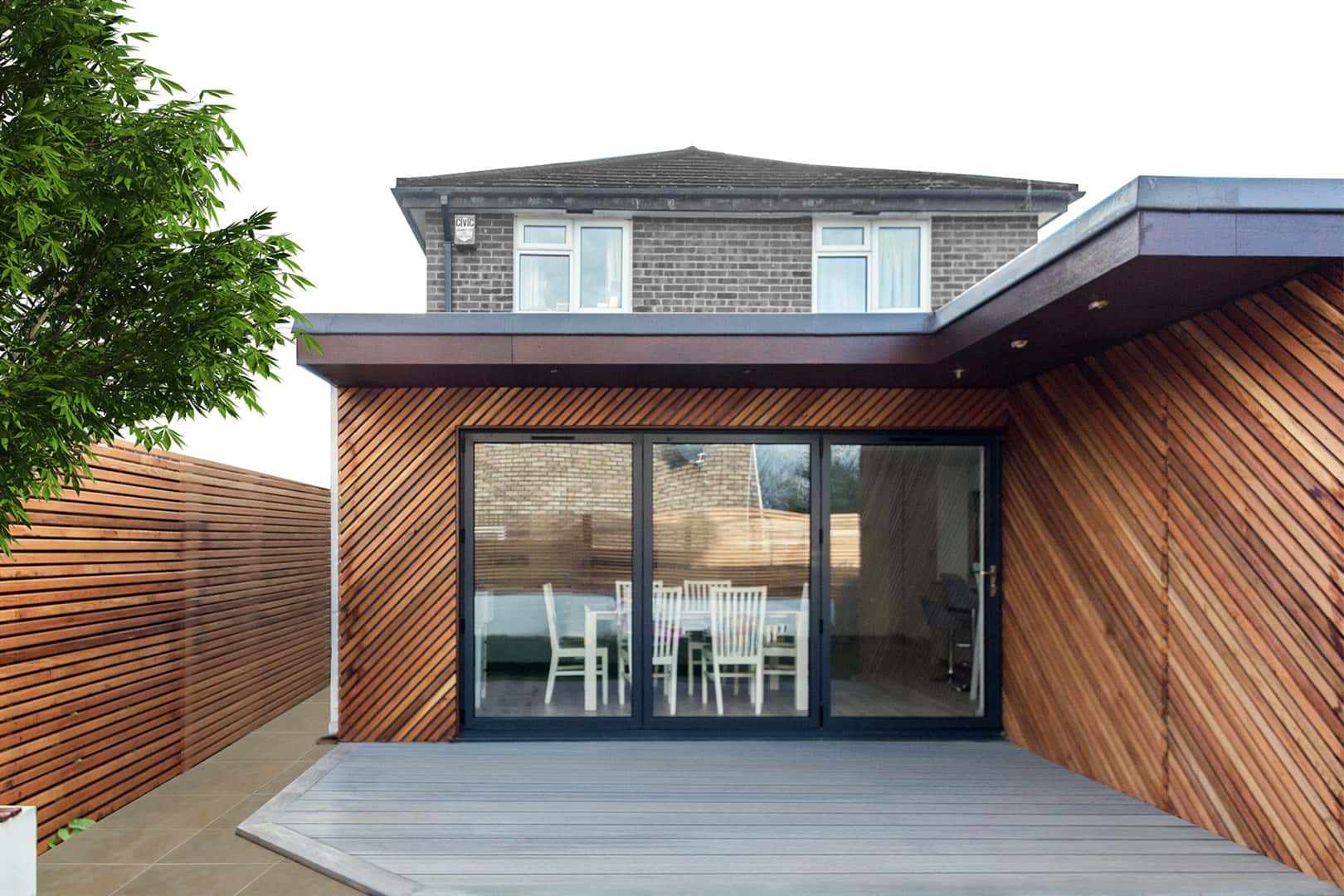
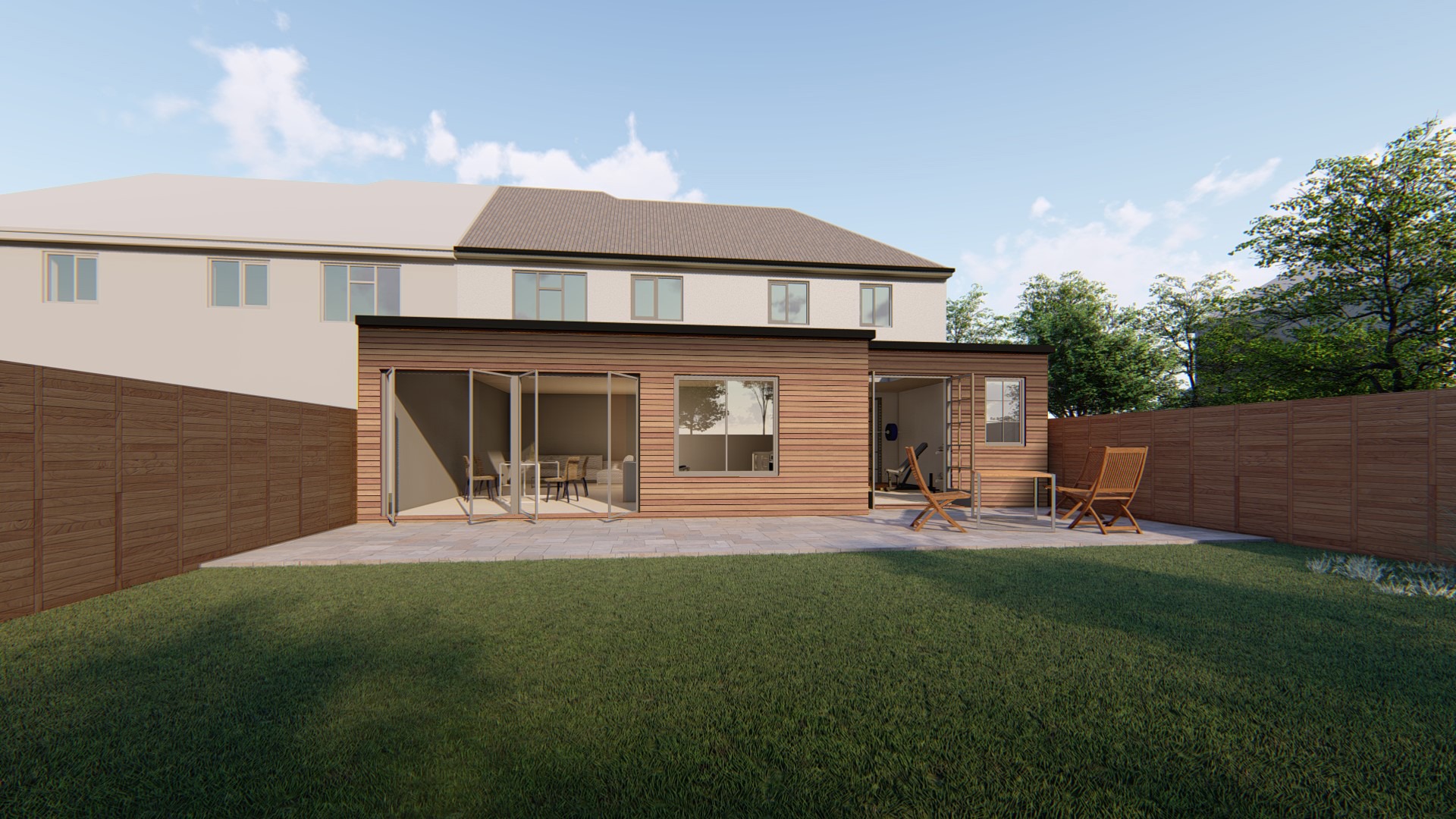
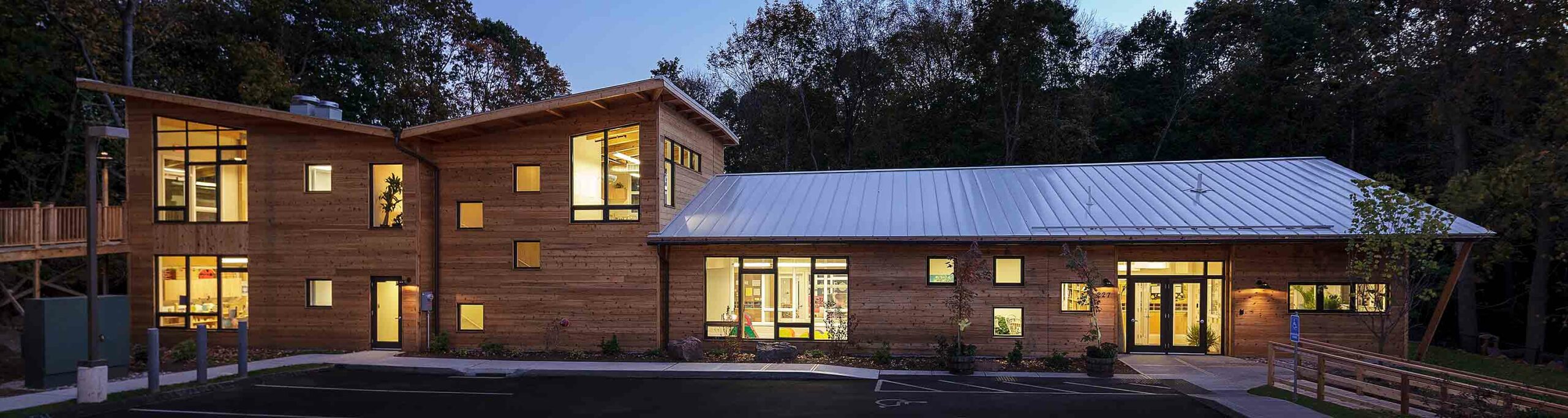
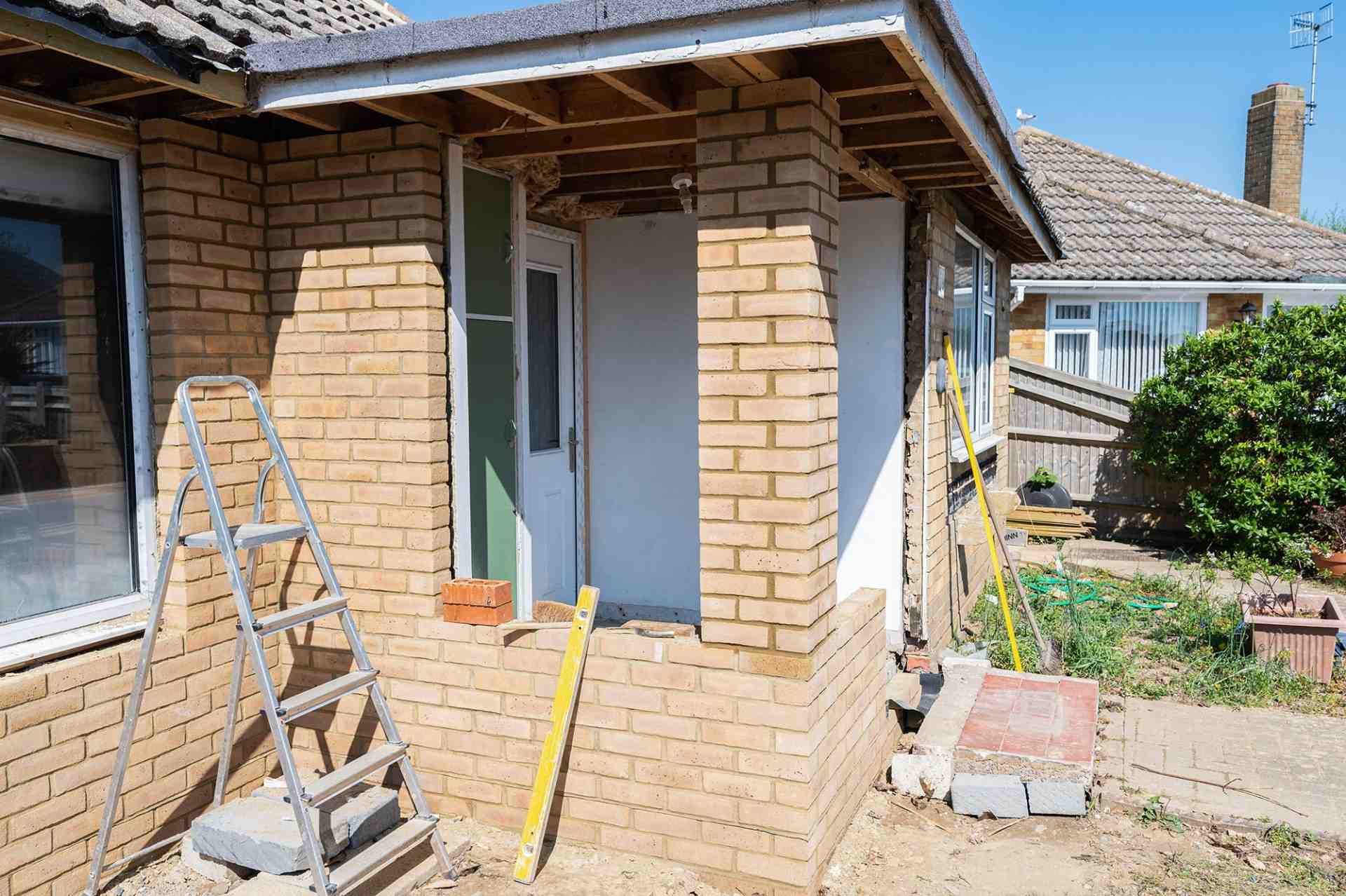
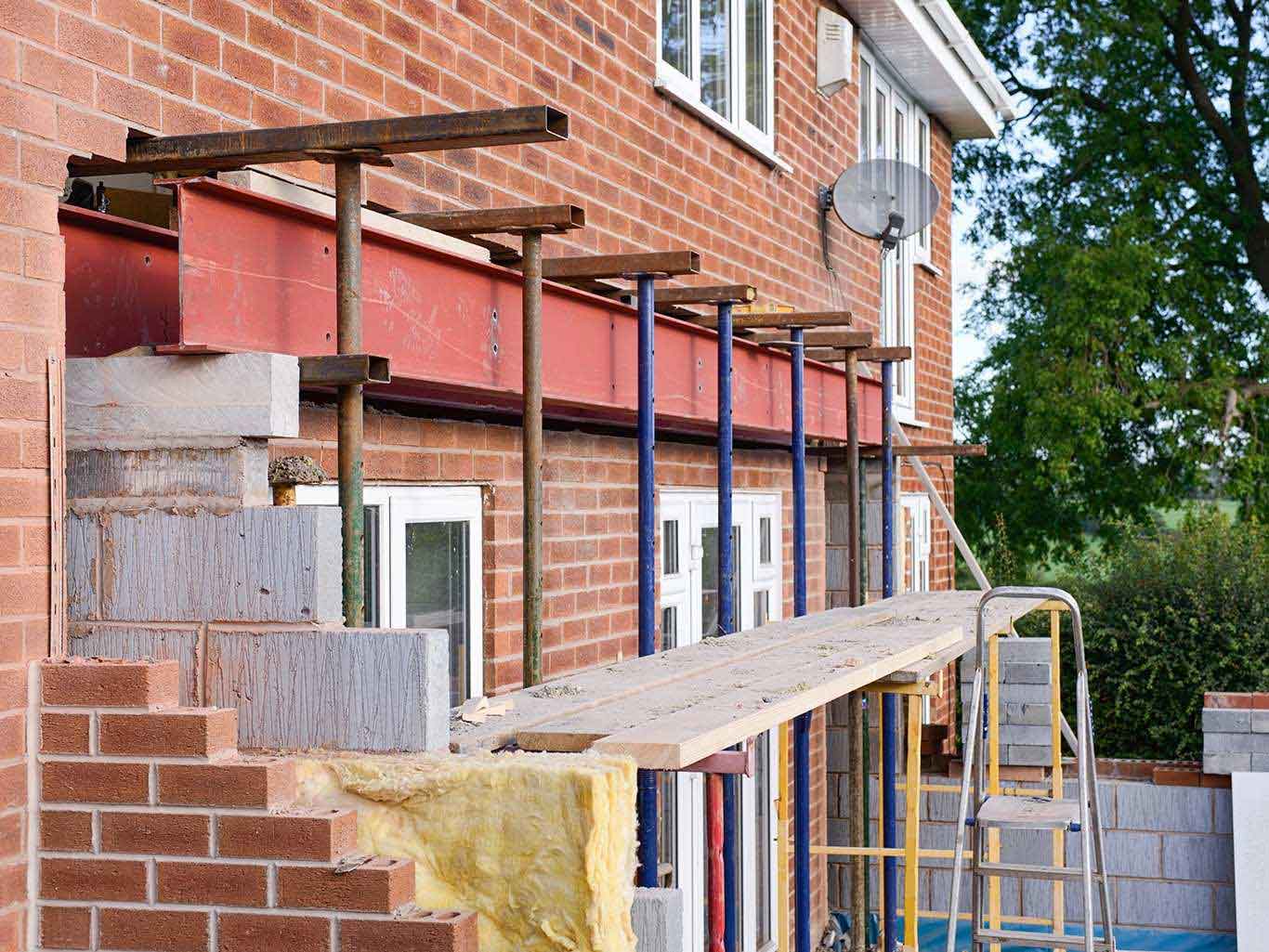
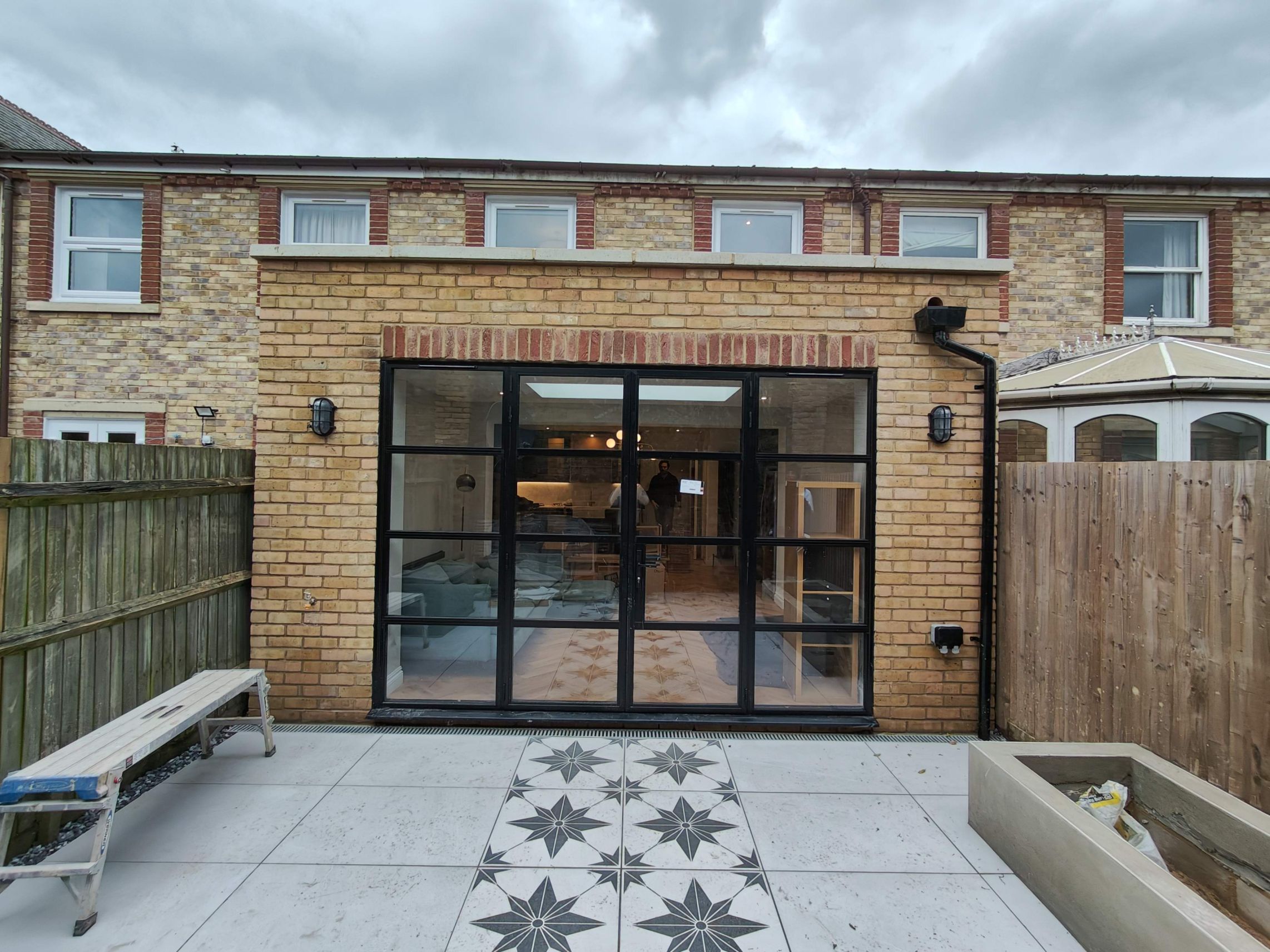
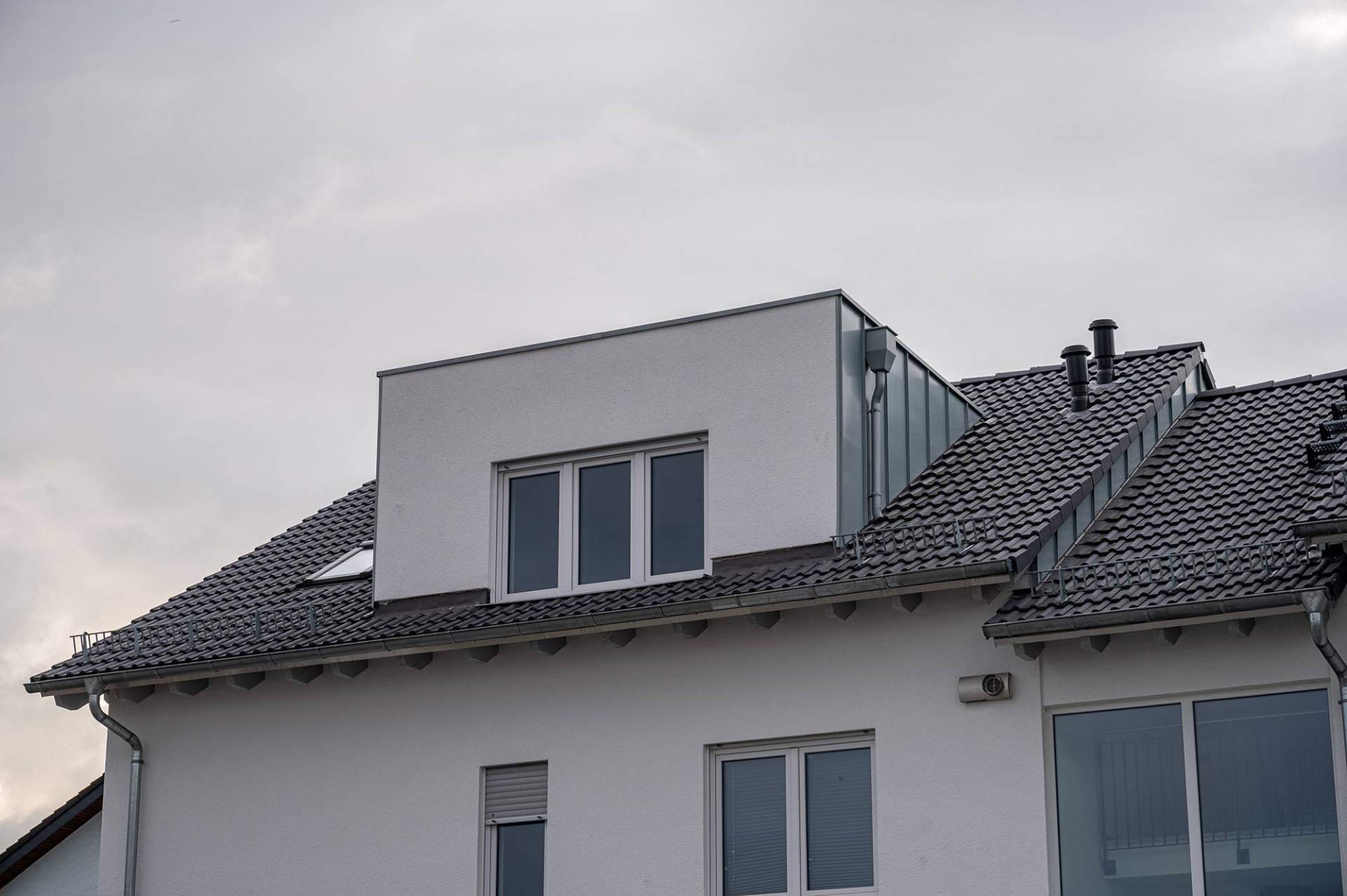
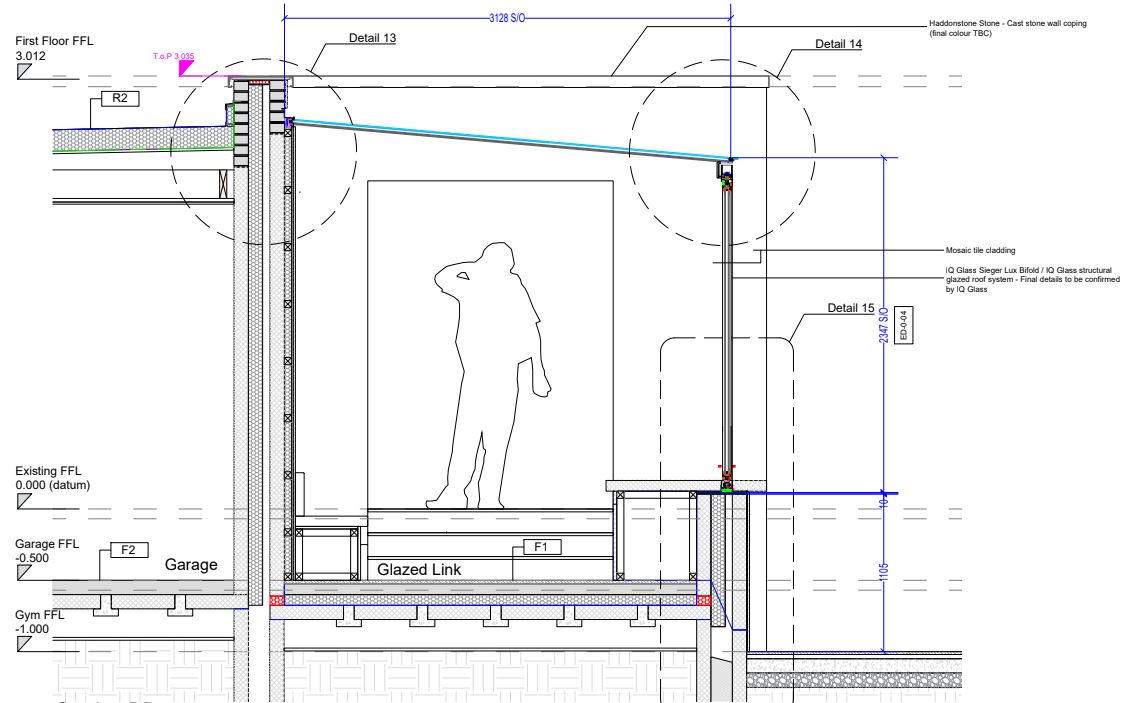
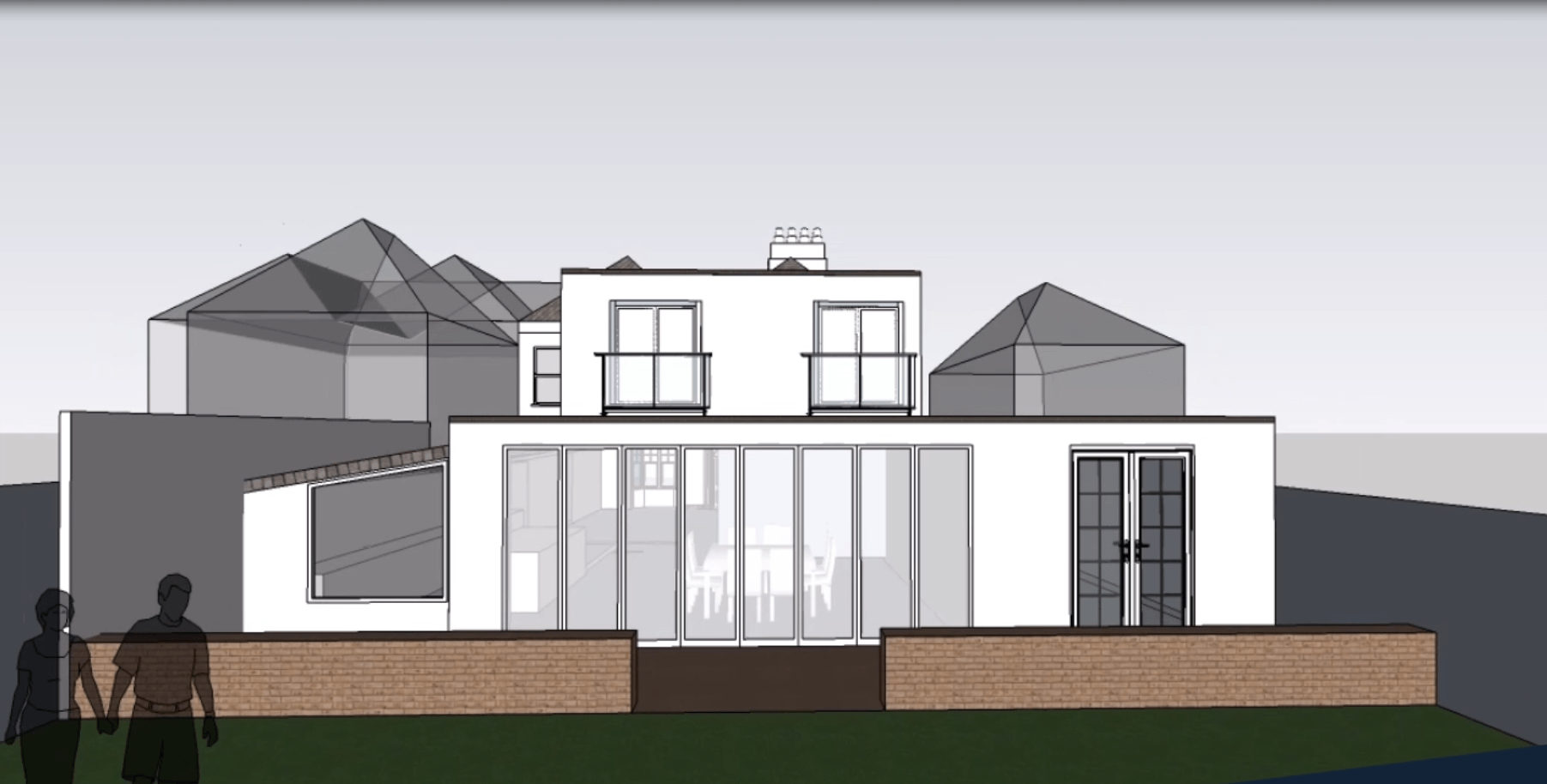
Walls and ceiling elements are built as prefabricated insulated panels ready to be transported on-site for erection. Cladding of timber frame structure (elaborated further in another section) is done with materials like bricks, fiber-cement panels, wood, or suitable tiles. The cladding is usually done both for decorative and insulative purposes (mostly to insulate the inner space from changing weather conditions).
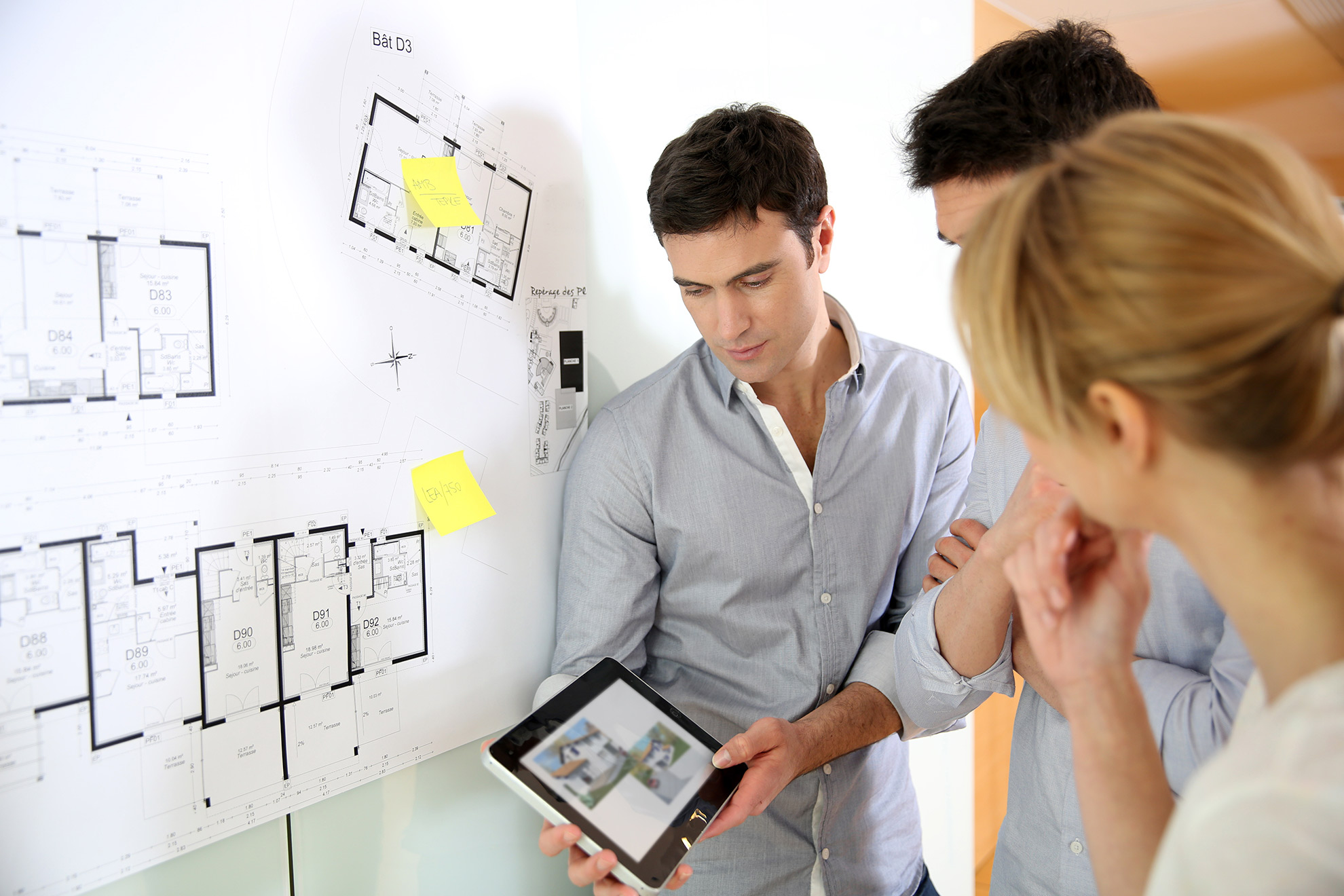
2. Design
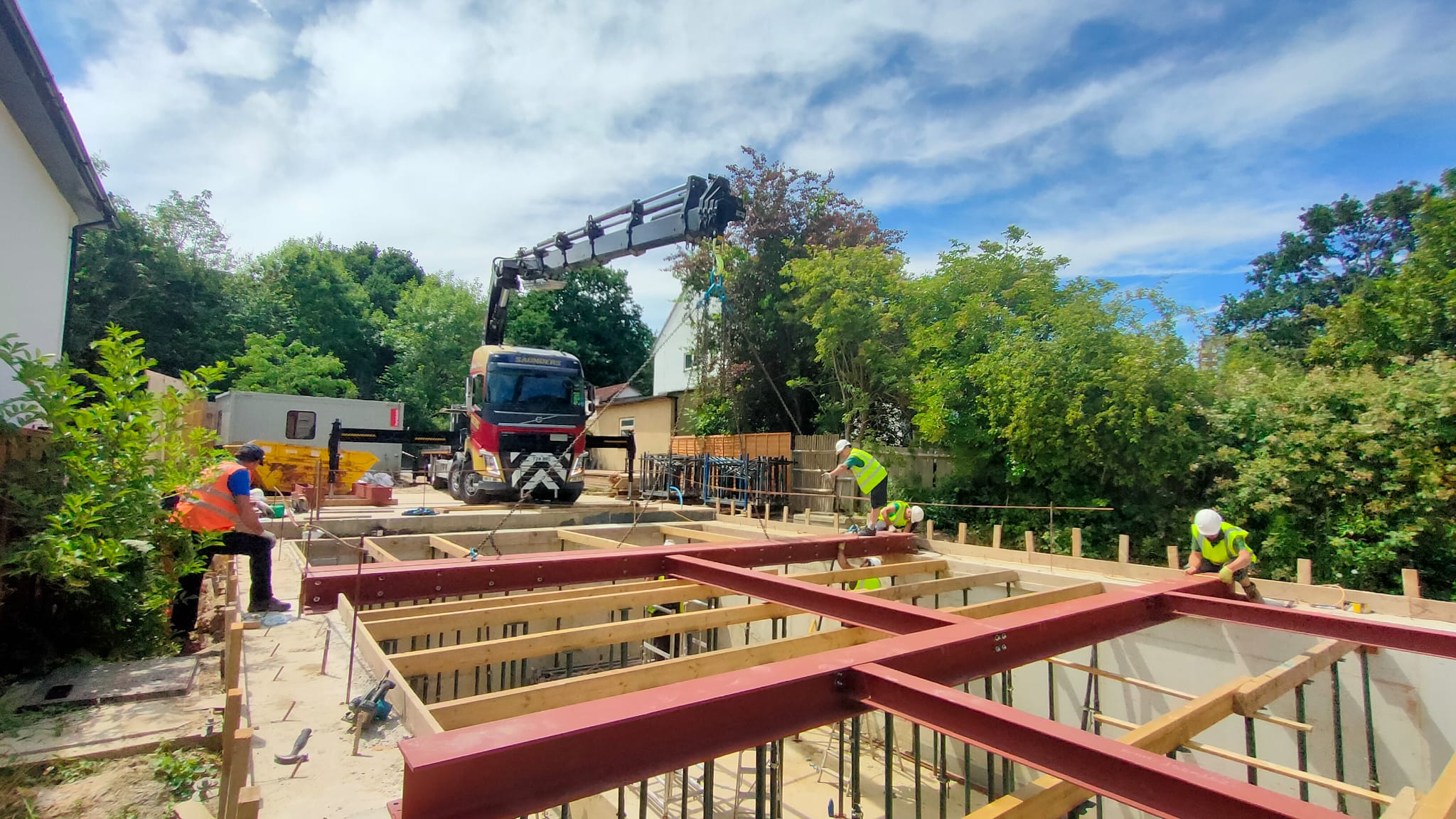
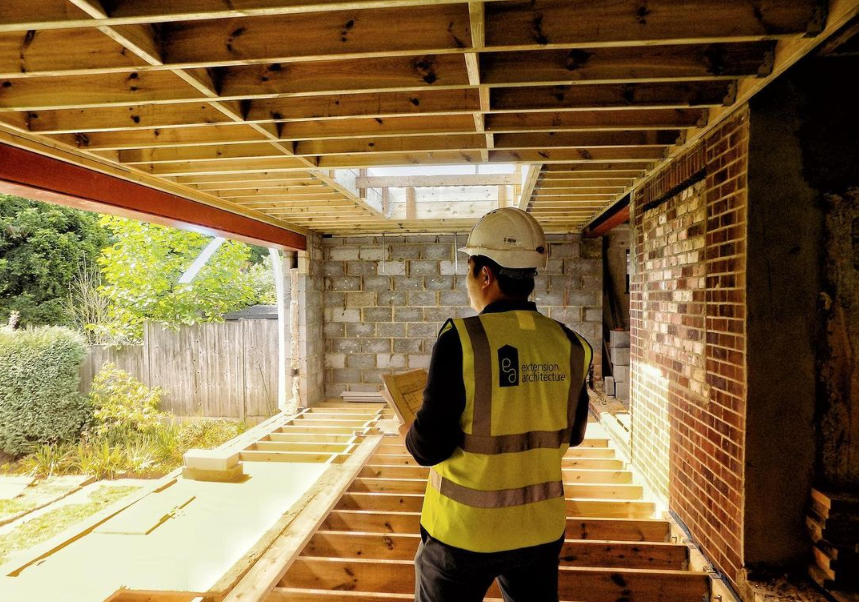
3. On-site Assembly
4. External Cladding
During cladding, considerations for ventilation to allow the escape of moisture are given. To protect the timber frame from harsh rains, and windy conditions, a breather membrane is used which resists the penetration of moisture.
Besides protective purposes, cladding is also done to enhance the aesthetic appeal of the building.
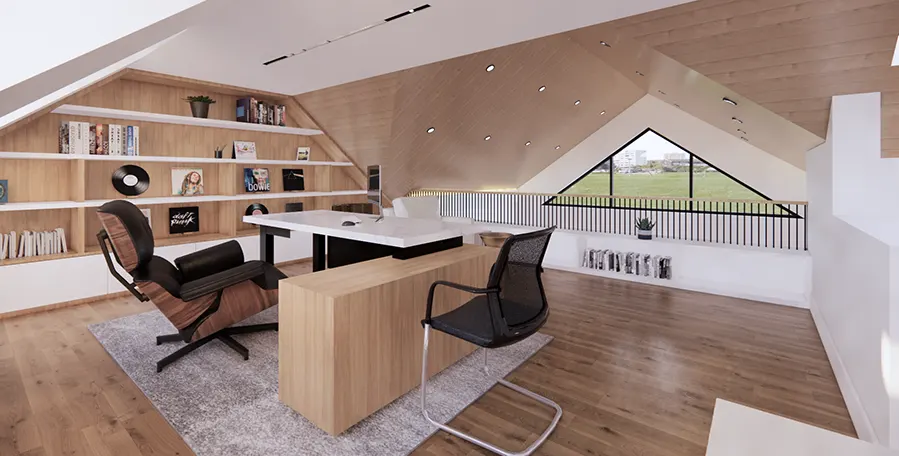
5. Internal Works
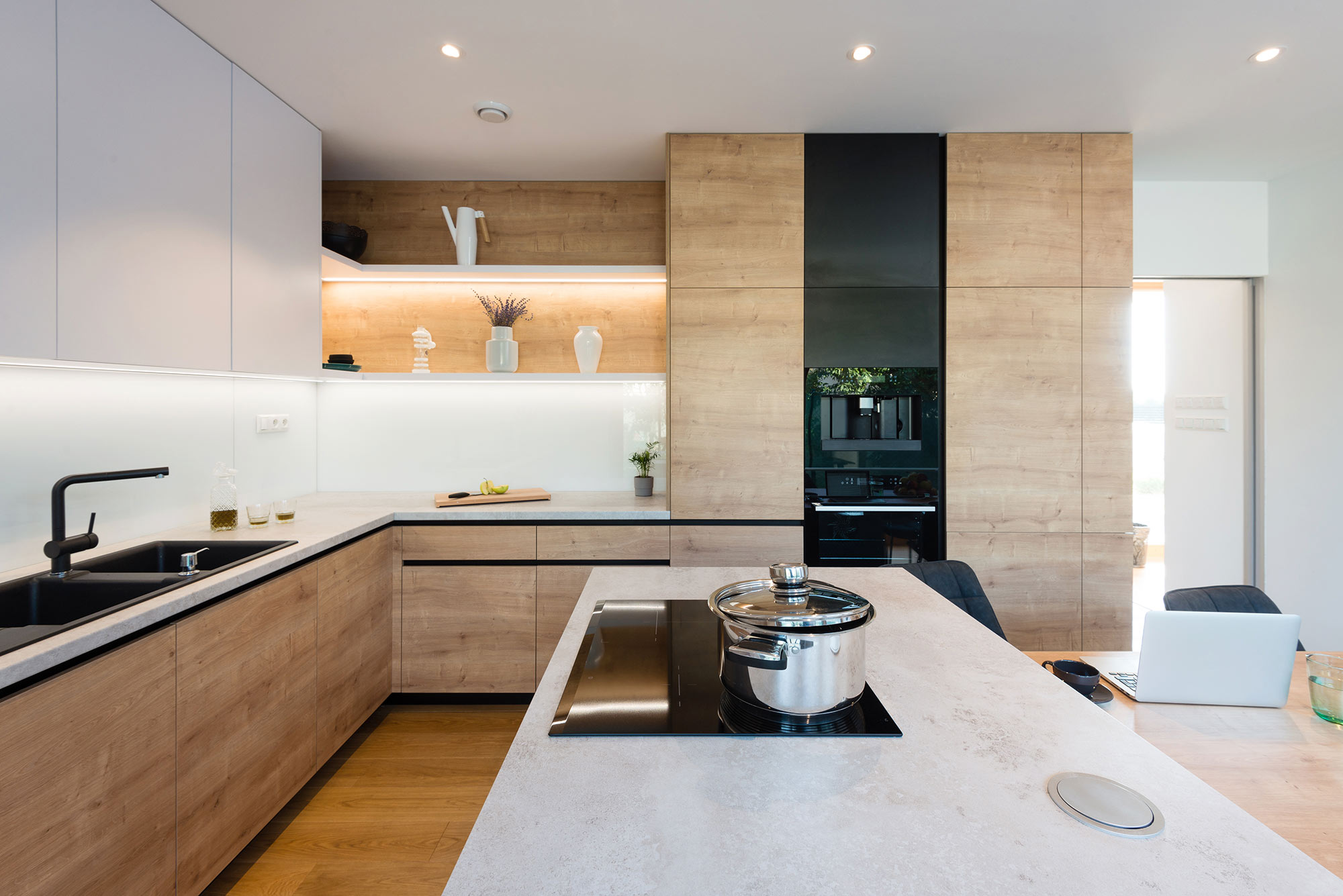
What are the Materials Used in Timber Frame Construction?
Below is a breakdown of the materials used –
1. Structural Timber
- Commonly used hardwoods – Pine, Douglas fir, Spruce
- Commonly used softwoods – Oak, Ash, Maple
- Glulam beams or Glue Laminated Timber for frames that involve large spans.
- Cross Laminated Timber (CLT) for walls, floors (for higher strength & durability).
- Laminated Veneer Lumber (LVL) are used as beams, rafters, studs, and purlins for floor joists, headers, and rim-boards.
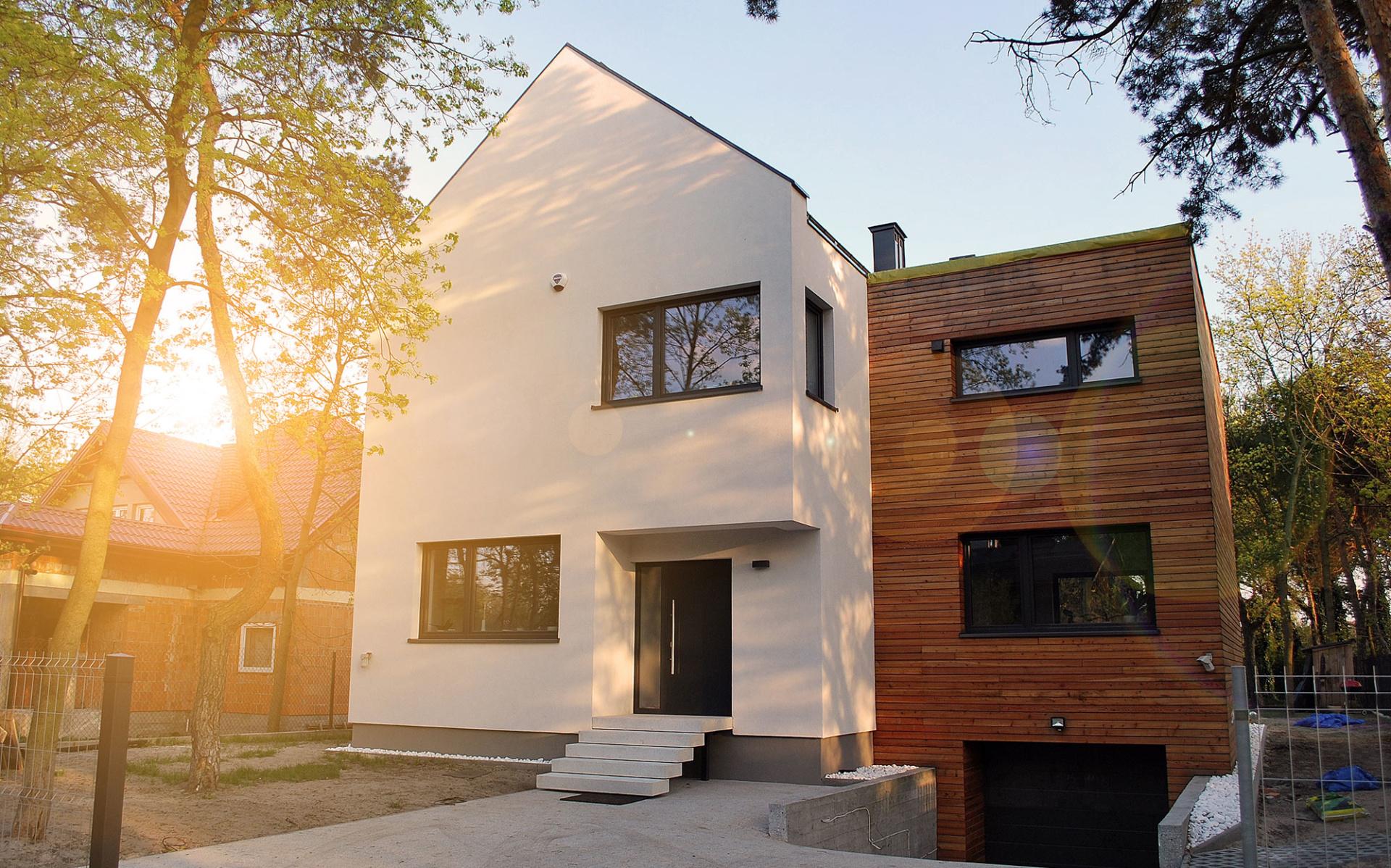
2. Cladding
- Timber cladding materials include softwoods like red cedar, pine, and larch. They offer good durability and resistance to decaying (especially red cedar).
Timber cladding requires regular maintenance in the form of painting and similar options to avoid discoloration and warping. - Metal cladding involves materials such as steel which is often a durable material or aluminium which is lightweight and anti-corrosive. Zinc can also be used for durability and sustainability.
- Composite cladding usually is a combination of different materials like wood, metal, and sometimes plastic. They can be more effective when the combination hits the right chord resulting in durability and low maintenance.
Fiber-cement is also used as a composite cladding material and is usually made of cellulose, cement, and other composites. They offer high durability, are moisture resistant, and require less maintenance. - Other cladding options like brick cladding and stone cladding are high on durability but can be expensive in terms of cost and maintenance.
Tile cladding and uPVC cladding though are cost-effective and low-maintenance options, they may not offer the strength required.
3. Sheathing
Materials used for sheathing –
- Oriented Strand Board (OSB)
- Plywood
- Cement Board
Additional Materials
- To improve the insulative characteristics and thermal performance of the structure, insulation materials such as cellulose, and mineral wool are usually used.
- To increase the structural strength of the superstructure, strip foundations are generally used that offer stability and sturdiness.
Cost of a Timber Frame Construction
The cost to build a timber frame house in the UK can range from £1,800 to £2,500 per sq metre.
The average total cost to build timber frame houses UK are as follows –
- A 2-bedroom timber frame house – £2,00,000
- 3-bedroom timber frame house – £2,50,000
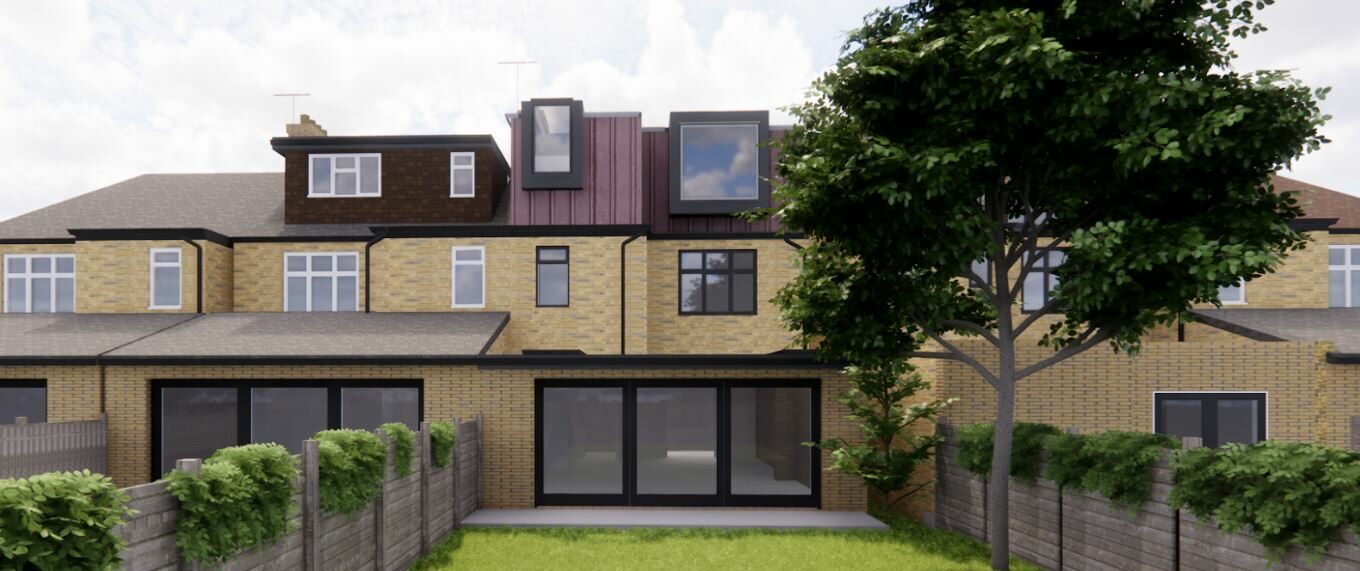
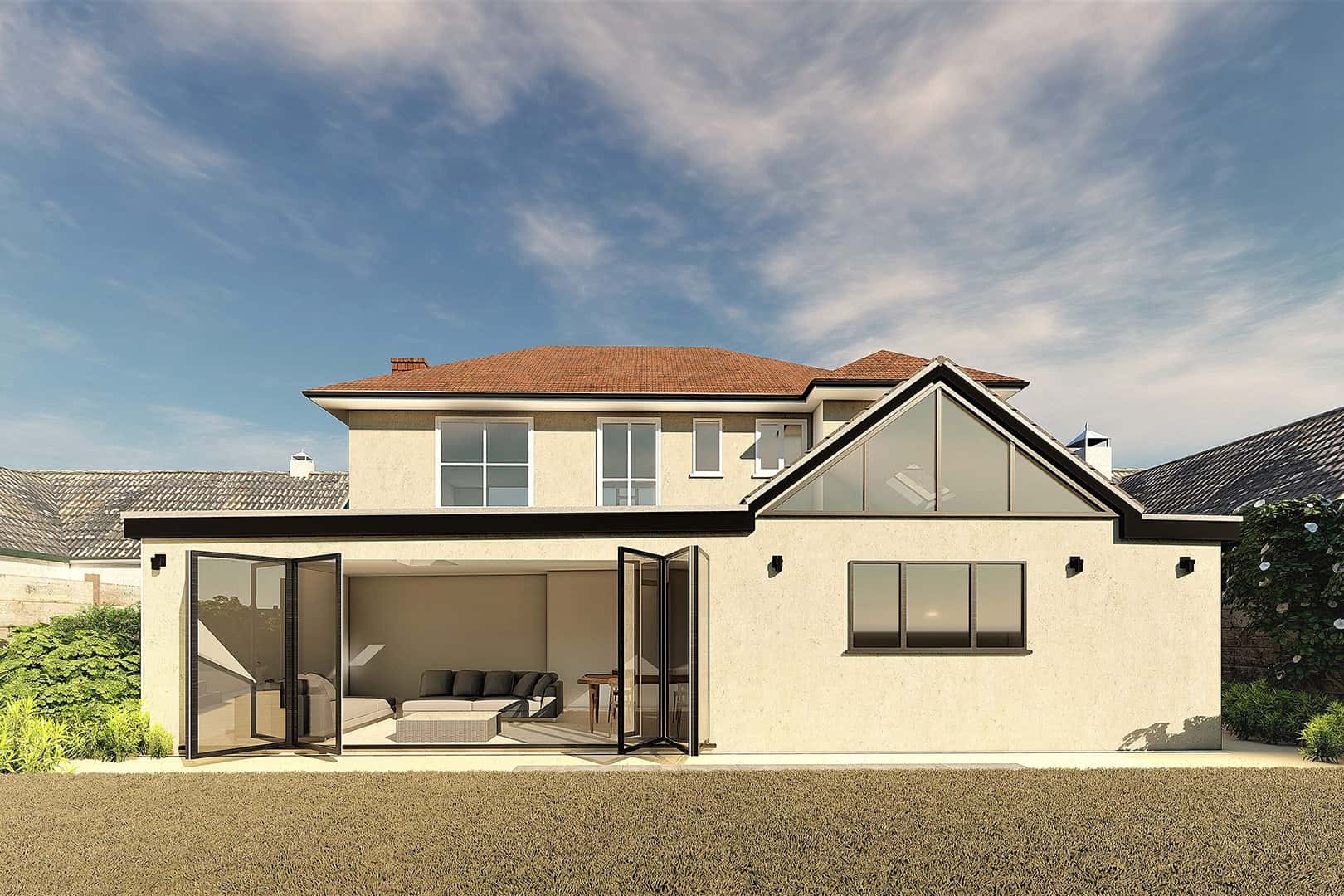
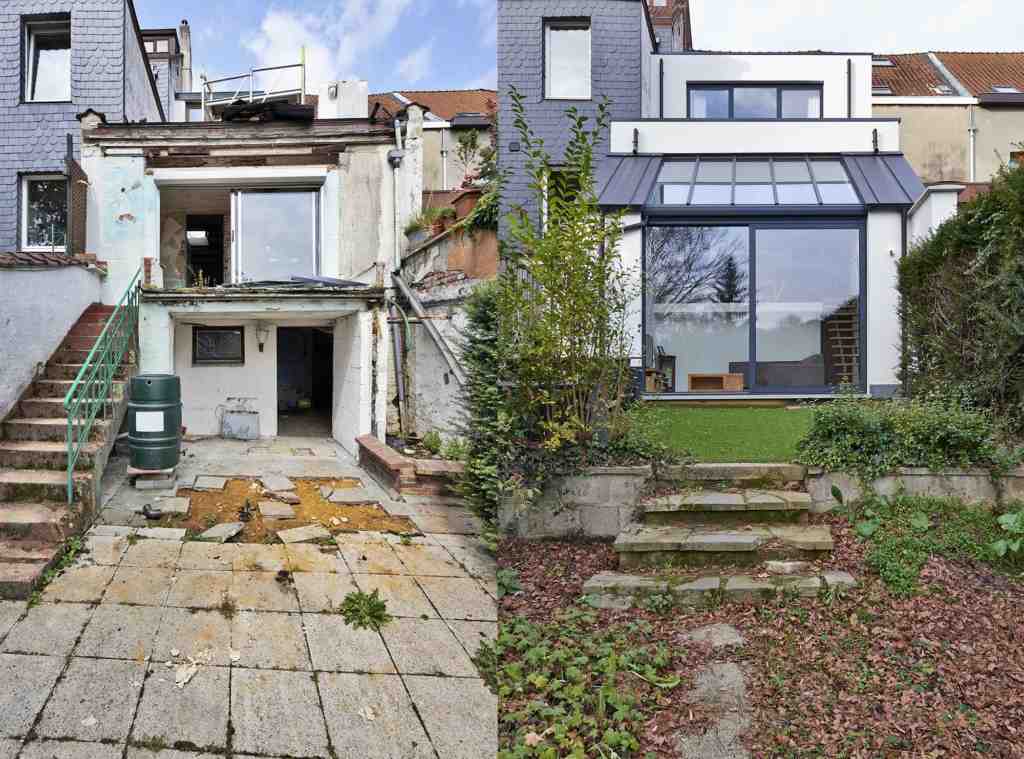
At Extension Architecture, we have the skill and expertise to take up your timber frame construction project; whether you are looking for a new build or a timber frame extension.
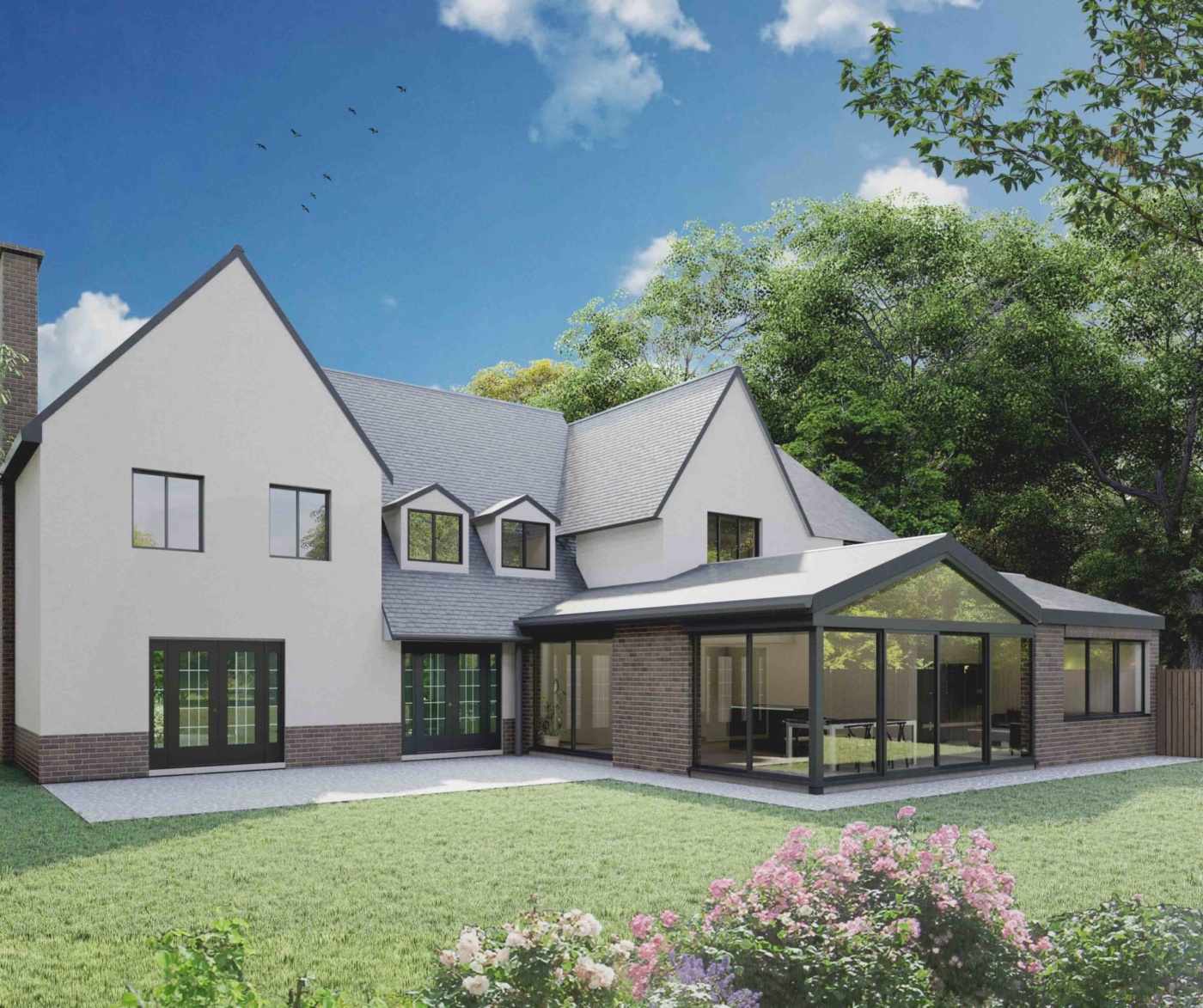
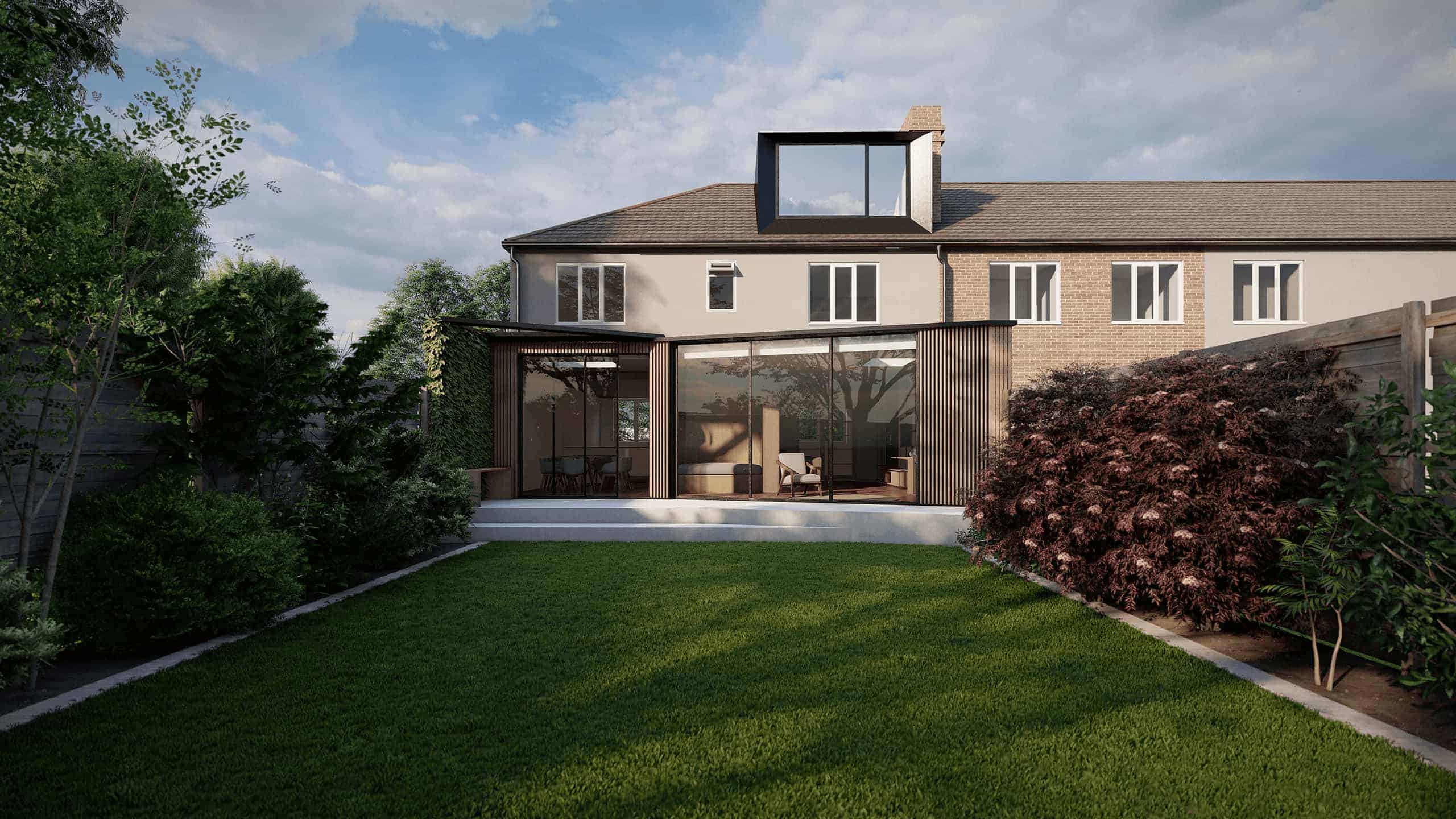
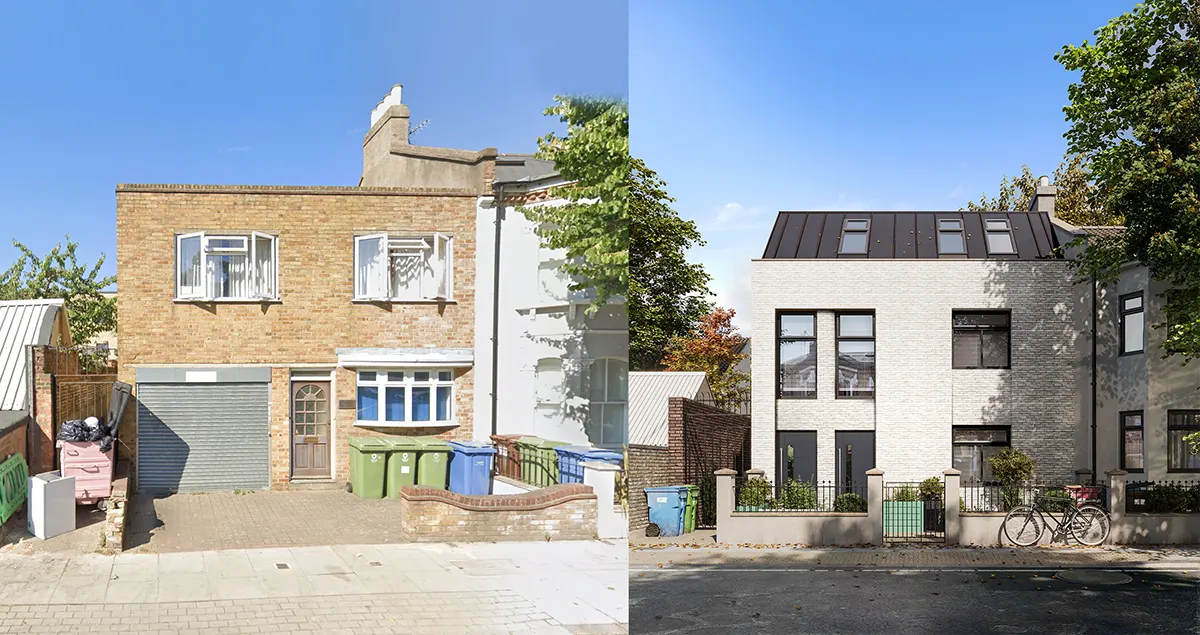
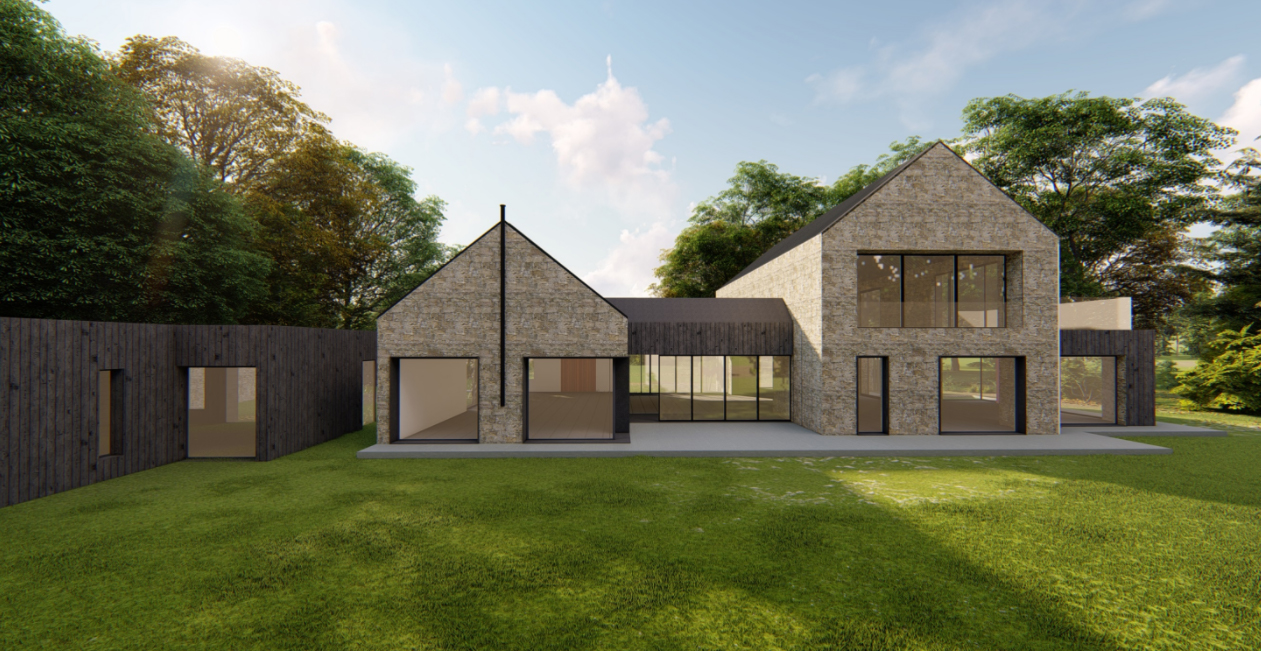
Traditional vs Modern Timber Frame Construction
- Traditional timber frame construction involves the use of solid timber beams that are joined using traditional joinery techniques.
Modern timber frame construction uses engineered wood as prefabricated panels and is joined using modern connectors.
- Traditional timber frame construction often is done on-site and requires highly skilled engineering and craftsmanship.
Modern timber frame construction is usually done off-site and involves precision engineering and other advanced techniques that help in faster assembly.
- Traditional timber frame constructions though are expensive, offer high durability and structural strength.
Modern timber frame constructions besides being less expensive and can last for generations and offer great value upon investment.
- Traditional methods are characterised by exposed beams and create a unique visual appeal.
Modern methods can be adapted to diverse aesthetic considerations and offer a warm and natural appeal.
- Traditional methods though focus on energy efficiency and sustainability may not offer the desired output in comparison to modern methods.
Modern methods offer excellent thermal performance and minimise heat loss and wastage.
Open Panel and Closed Panel Systems
Important Considerations for Timber Frame Construction
1. Structural
2. Area/Scale of the Building
3. Climate
Benefits of Timber Frame Construction
- Sustainability
Timber frame structures require less energy than other means such as concrete or steel and hence contribute to high energy efficiency and reduced carbon emissions. - Time Taken to Build
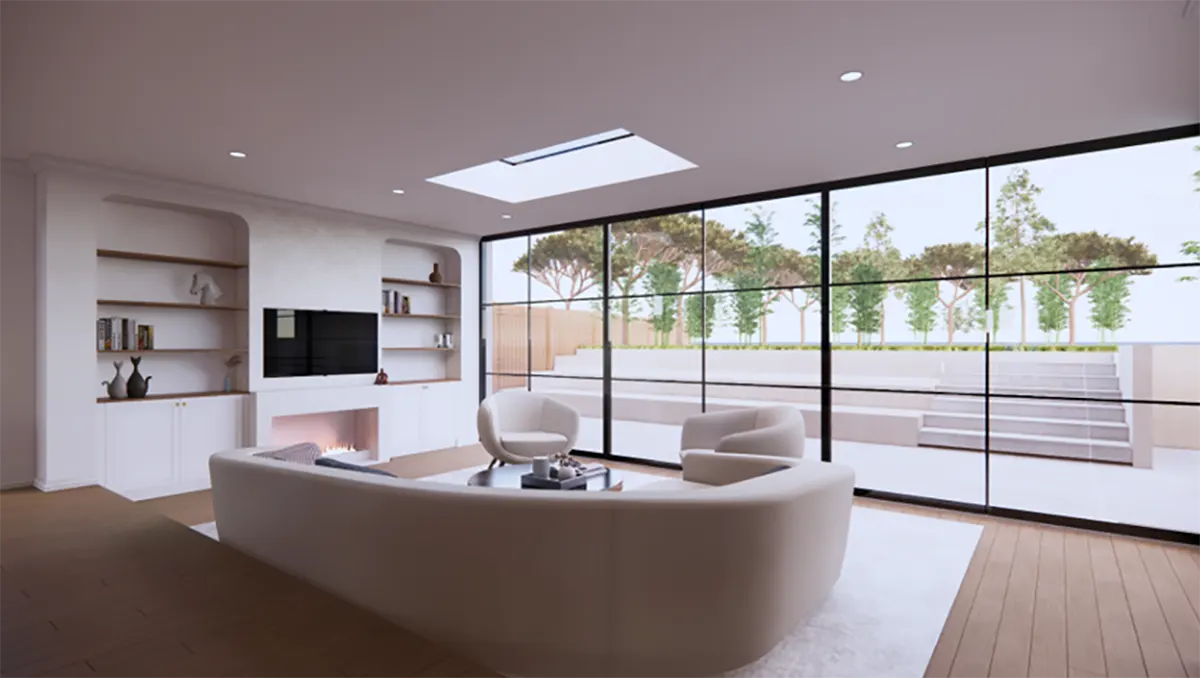
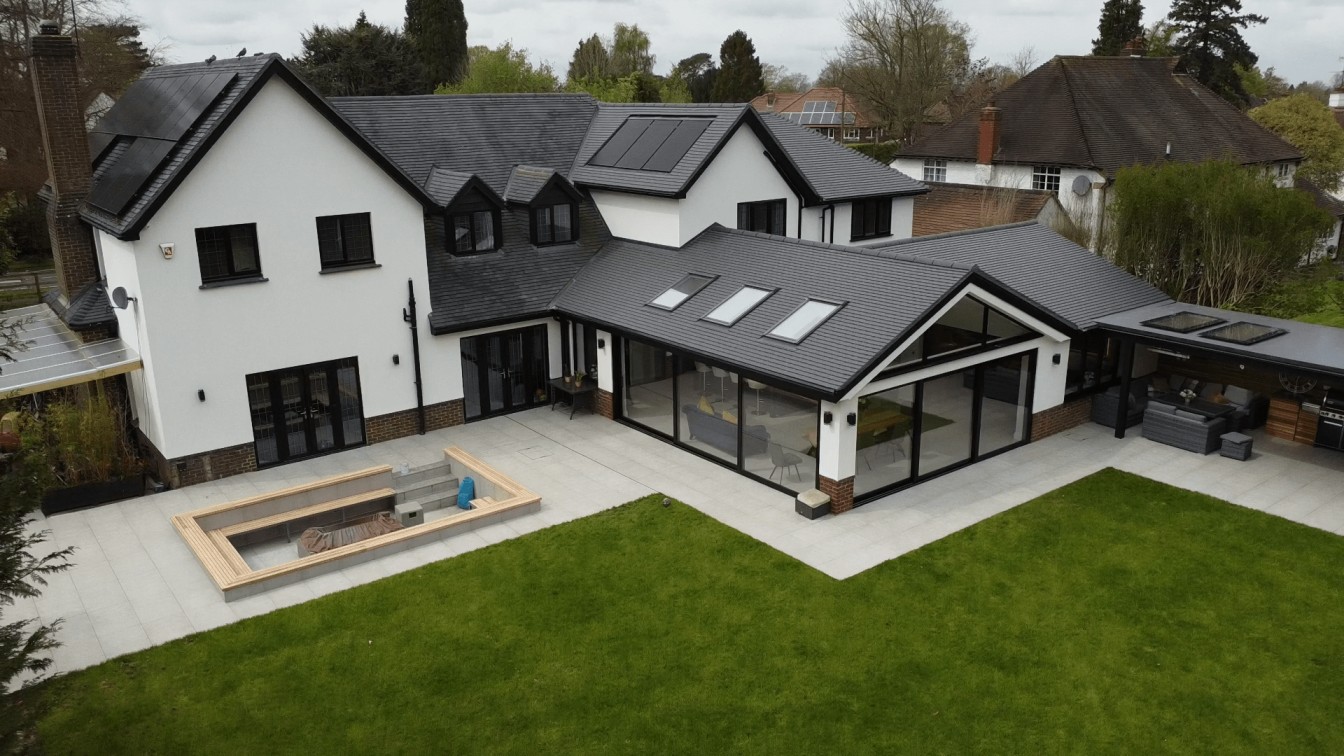
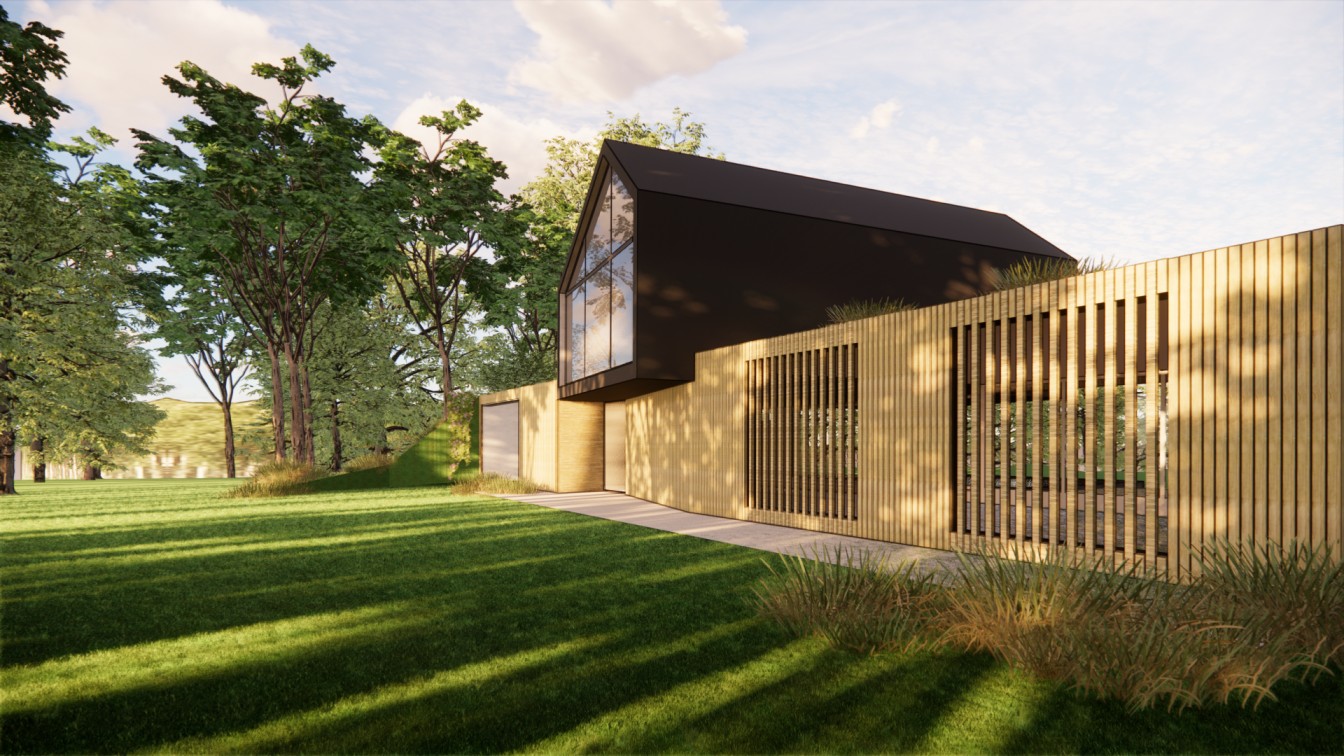
As timber frames are manufactured off-site in a controlled and mechanised environment, they can be quickly erected on-site saving significant time on other internal and external jobs. - Aesthetic Style
Timber frames can be adapted to suit diverse architectural styles. From the barn-like rustic look with exposed beams to fit into the idea of a modern living space. With the use of precision engineering and modern methods, these panels can be designed to any style. - Thermal Properties
Timber is a great insulator and is a slow absorber of heat. Besides that, with all the sheathing and air-tight construction, the level of thermal performance only increases and thus offers excellent thermal properties.
Besides the above benefits, timber frame constructions are excellent in insulating noise and ensure maintenance of optimal acoustic levels inside the building. They are also less invasive to the environment because of their structural durability which can last for decades and even generations.
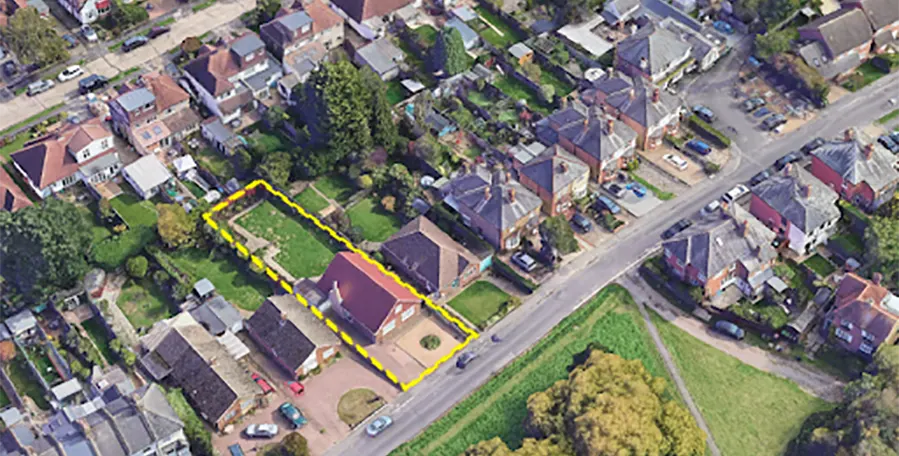
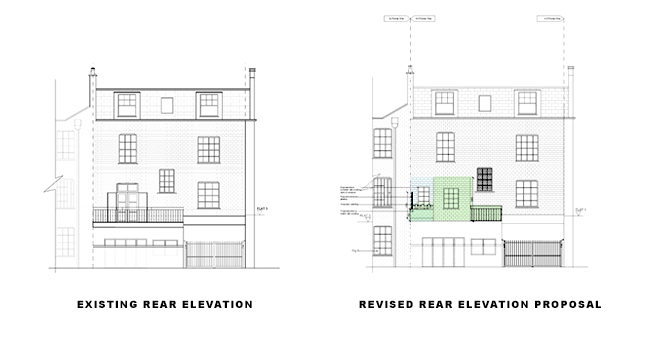
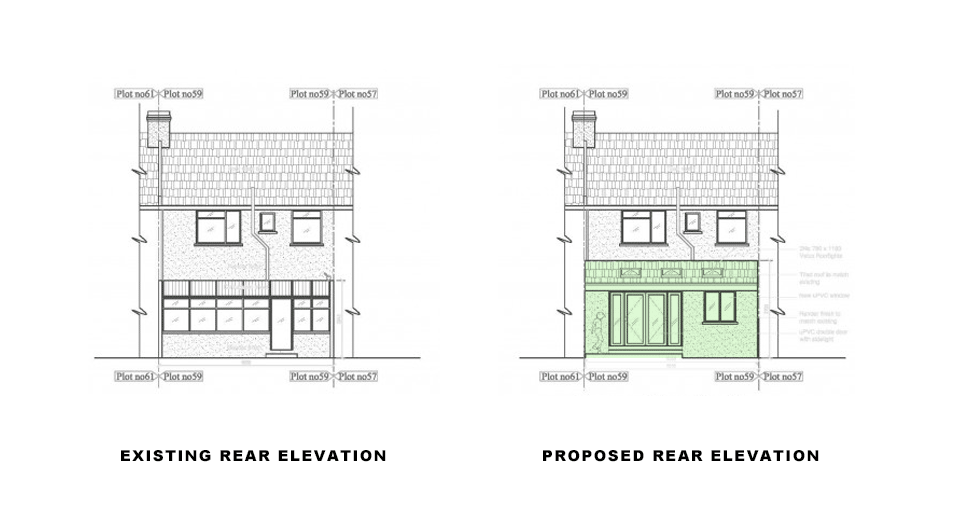
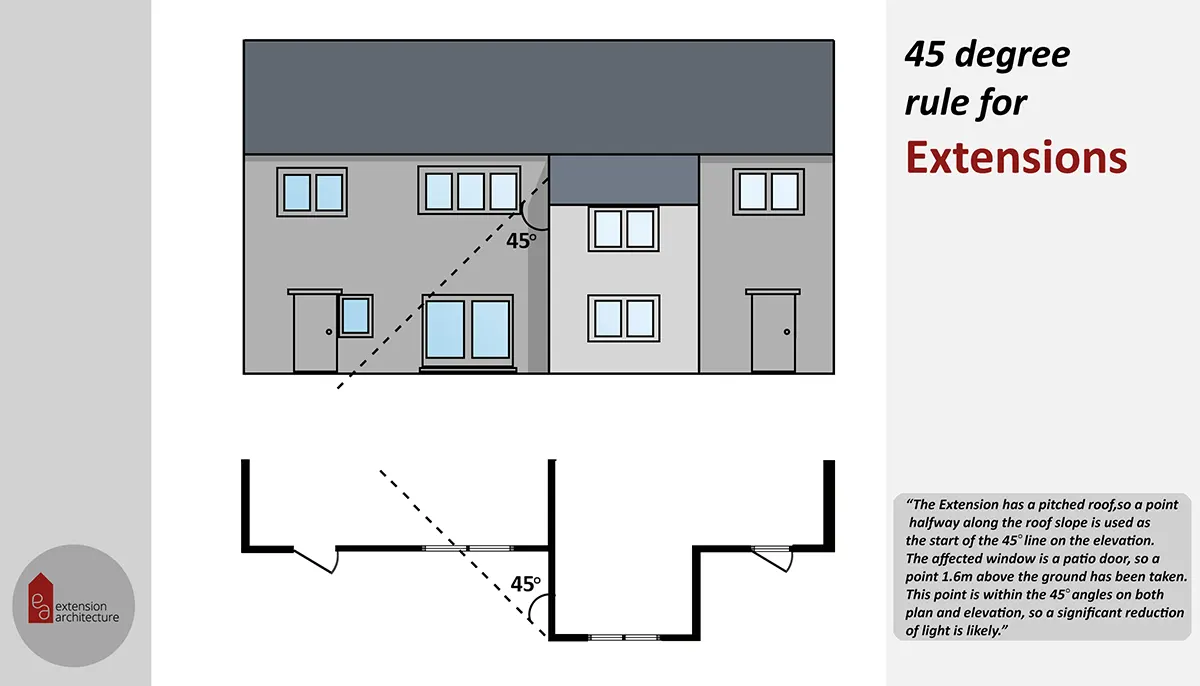
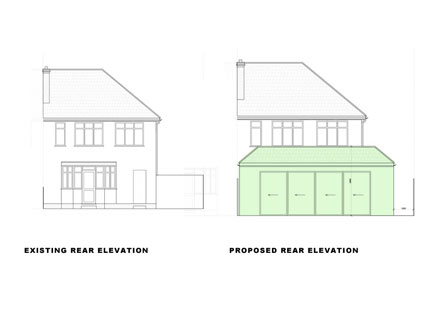
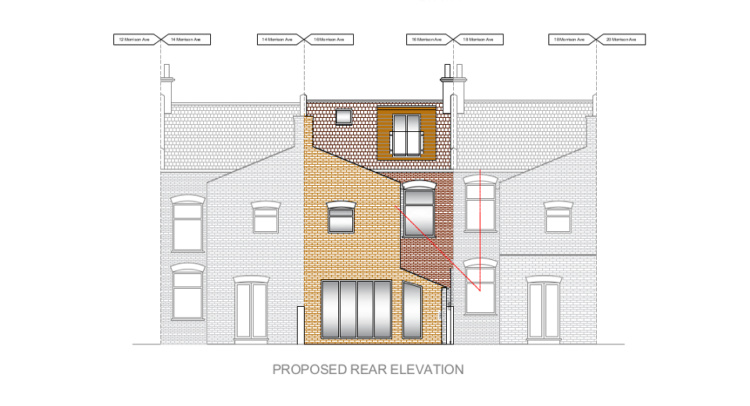
Planning Permission for Timber Frame Construction
Conclusion
If you are planning for a timber frame house, you have the best experts to guide you at Extension Architecture. Our RIBA chartered architects are proficient and industrious in all types of construction projects including timber frame buildings.
With a keen eye for energy efficiency, our architects ensure every project contributes to the environment and delivers on longevity and quality while also weighing lighter on your budget. Contact us for the more details.